Influenza A Virus Infection Triggers Pyroptosis and Apoptosis of Respiratory Epithelial Cells through the Type I Interferon Signaling Pathway in a Mutually Exclusive Manner
- PMID: 29743359
- PMCID: PMC6026744
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00396-18
Influenza A Virus Infection Triggers Pyroptosis and Apoptosis of Respiratory Epithelial Cells through the Type I Interferon Signaling Pathway in a Mutually Exclusive Manner
Abstract
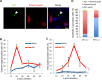
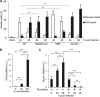
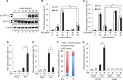
Respiratory epithelial cell death by influenza virus infection is responsible for the induction of inflammatory responses, but the exact cell death mechanism is not understood. Here we showed that influenza virus infection induces apoptosis and pyroptosis in normal or precancerous human bronchial epithelial cells. Apoptosis was induced only in malignant tumor cells infected with influenza virus. In human precancerous respiratory epithelial cells (PL16T), the number of apoptotic cells increased at early phases of infection, but pyroptotic cells were observed at late phases of infection. These findings suggest that apoptosis is induced at early phases of infection but the cell death pathway is shifted to pyroptosis at late phases of infection. We also found that the type I interferon (IFN)-mediated JAK-STAT signaling pathway promotes the switch from apoptosis to pyroptosis by inhibiting apoptosis possibly through the induced expression of the Bcl-xL anti-apoptotic gene. Further, the inhibition of JAK-STAT signaling repressed pyroptosis but enhanced apoptosis in infected PL16T cells. Collectively, we propose that type I IFN signaling pathway triggers pyroptosis but not apoptosis in the respiratory epithelial cells in a mutually exclusive manner to initiate proinflammatory responses against influenza virus infection.IMPORTANCE Respiratory epithelium functions as a sensor of infectious agents to initiate inflammatory responses along with cell death. However, the exact cell death mechanism responsible for inflammatory responses by influenza virus infection is still unclear. We showed that influenza virus infection induced apoptosis and pyroptosis in normal or precancerous human bronchial epithelial cells. Apoptosis was induced at early phases of infection, but the cell death pathway was shifted to pyroptosis at late phases of infection under the regulation of type I IFN signaling to promote proinflammatory cytokine production. Taken together, our results indicate that the type I IFN signaling pathway plays an important role to induce pyroptosis but represses apoptosis in the respiratory epithelial cells to initiate proinflammatory responses against influenza virus infection.
Keywords: apoptosis; pyroptosis; respiratory epithelial cells; type I IFN signaling.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

