qSR: a quantitative super-resolution analysis tool reveals the cell-cycle dependent organization of RNA Polymerase I in live human cells
- PMID: 29743503
- PMCID: PMC5943247
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-25454-0
qSR: a quantitative super-resolution analysis tool reveals the cell-cycle dependent organization of RNA Polymerase I in live human cells
Abstract
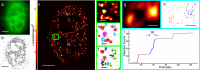
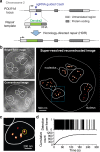
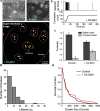
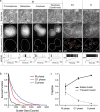
We present qSR, an analytical tool for the quantitative analysis of single molecule based super-resolution data. The software is created as an open-source platform integrating multiple algorithms for rigorous spatial and temporal characterizations of protein clusters in super-resolution data of living cells. First, we illustrate qSR using a sample live cell data of RNA Polymerase II (Pol II) as an example of highly dynamic sub-diffractive clusters. Then we utilize qSR to investigate the organization and dynamics of endogenous RNA Polymerase I (Pol I) in live human cells, throughout the cell cycle. Our analysis reveals a previously uncharacterized transient clustering of Pol I. Both stable and transient populations of Pol I clusters co-exist in individual living cells, and their relative fraction vary during cell cycle, in a manner correlating with global gene expression. Thus, qSR serves to facilitate the study of protein organization and dynamics with very high spatial and temporal resolutions directly in live cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Abràmoff MD, Magalhães PJ, Ram SJ. Image processing with imageJ. Biophotonics International. 2004;11:36–41.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

