Combination of anti-vascular agent - DMXAA and HIF-1α inhibitor - digoxin inhibits the growth of melanoma tumors
- PMID: 29743548
- PMCID: PMC5943409
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-25688-y
Combination of anti-vascular agent - DMXAA and HIF-1α inhibitor - digoxin inhibits the growth of melanoma tumors
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Combination of anti-vascular agent - DMXAA and HIF-1α inhibitor - digoxin inhibits the growth of melanoma tumors.Sci Rep. 2020 Mar 25;10(1):5698. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-62440-x. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32210342 Free PMC article.
Abstract
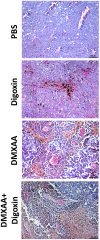
Vascular disrupting agents as DMXAA inhibit tumor growth only for a short period of time followed by rapid tumor regrowth. Among others, hypoxia and presence of transcription factor HIF-1α are responsible for tumors regrowth. The aim of our study was to investigate the inhibition of murine melanoma growth by combining two agents: anti-vascular - DMXAA and the HIF-1α inhibitor - digoxin and explaining the mechanism of action of this combination. After DMXAA treatment tumor size was reduced only for a limited time. After 7 days regrowth of tumors was observed and number of vessels was increased especially in tumor's peripheral areas. DMXAA also induced an influx of immune cells: macrophages, CD8+ cytotoxic lymphocytes, NK cells, CD4+ lymphocytes. Administration of digoxin alone inhibited the growth of tumors. Administration of both agents in the proper sequence significantly inhibited the regrowth of tumors better than either agents alone. Combination therapy reduced number of newly formed vessels. In tumors of mice treated with combination therapy, the number of macrophages M1, CD8+ cytotoxic lymphocytes, NK cells and to a lesser extent CD4+ cells was increased. The combination of anti-vascular agents with HIF-1α inhibitors appears to be an effective therapeutic option.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

