Inhibition of Spontaneous Contractility of Isolated Caprine Ureter by Flupirtine
- PMID: 29744325
- PMCID: PMC5932919
- DOI: 10.4103/ijabmr.IJABMR_159_17
Inhibition of Spontaneous Contractility of Isolated Caprine Ureter by Flupirtine
Abstract
Context: Kv7 potassium channels are expressed in several types of smooth muscles and could mediate physiological responses in the tissues expressed. Flupirtine is an analgesic that acts by opening Kv7 potassium channels. It has been shown to inhibit the contractility of several types of isolated smooth muscle.
Aims: This study investigated the ability of flupirtine to inhibit the spontaneous contractility of isolated distal caprine (goat) ureter.
Settings and design: Spontaneous contractility of the isolated goat ureter was recorded using a physiograph.
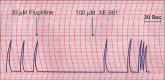
Materials and methods: The ability of 1, 3, 10, 30, and 90 μM concentrations of flupirtine maleate to inhibit the spontaneous contractility of isolated distal goat ureter was investigated. The ability of the nonspecific potassium channel blocker 4-aminopyridine (4-AP; 1 mM) and the specific Kv7 channel blocker XE-991 (100 μM) to reverse the inhibitory effect of flupirtine on ureteric contractility was also investigated.
Statistical analysis used: Both parametric and nonparametric statistical tests were used.
Results: At 10, 30, and 90 μM concentrations, flupirtine significantly inhibited the spontaneous contractility of the isolated goat ureter. The EC50 of flupirtine for a contact period of 10 min was 17.7 μM. The inhibitory effect of flupirtine on ureteric contractility was significantly reversed by 4-AP and XE-991.
Conclusions: Flupirtine inhibits the spontaneous contractility of the isolated goat ureter by opening Kv7 channels.
Keywords: Contractility; Kv7channel; flupirtine; isolated; ureter.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources