Changes in MiRNA-5196 Expression as a Potential Biomarker of Anti-TNF-α Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients
- PMID: 29744553
- PMCID: PMC6154007
- DOI: 10.1007/s00005-018-0513-y
Changes in MiRNA-5196 Expression as a Potential Biomarker of Anti-TNF-α Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients
Abstract
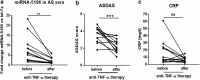
In this study, we analysed the expression level of sera circulating miRNA-5196 in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and ankylosing spondylitis (AS) patients before and after tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α therapy as biomarkers predicting positive treatment outcome. We enrolled 10 RA patients, 13 AS patients, and 12 healthy individuals in the study. The expression of miRNA-5196 was measured by real-time polymerase chain reaction before and after anti-TNF-α therapy. Disease activity of RA patients was assessed using disease activity score 28 (DAS28), whereas ankylosing spondylitis DAS (ASDAS) was used in AS patients. MiRNA-5196 expression was significantly higher in patients with RA and AS before TNF-α therapy than in those following anti-TNF-α therapy and healthy controls. Changes in miRNA-5196 expression positively correlated with delta DAS28 or delta ASDAS, respectively, following TNF-α therapy. In contrast, changes in C-reactive protein (CRP) levels in RA and AS patients did not positively correlate with DAS28 or ASDAS changes. Receiver-operating characteristic analysis showed better diagnostic accuracy of miRNA-5196 expression both in RA (area under curve (AUC) = 0.87, p = 0.055) and AS patients (AUC = 0.90, p = 0.050) compared to CRP levels in RA (AUC = 0.75, p = 0.201) and AS patients (AUC = 0.85, p = 0.086) upon biologic therapy treatment. Finding novel biomarkers, including miRNA-5196 which allow to predict and monitor anti-TNF-α response, would be of clinical value especially during the early phase of RA or AS development.
Keywords: Ankylosing spondylitis; Anti-TNF-α; Biologic therapy; Biomarker; MiRNA; Rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



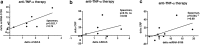

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

