Compounds from African Medicinal Plants with Activities Against Selected Parasitic Diseases: Schistosomiasis, Trypanosomiasis and Leishmaniasis
- PMID: 29744736
- PMCID: PMC5971035
- DOI: 10.1007/s13659-018-0165-y
Compounds from African Medicinal Plants with Activities Against Selected Parasitic Diseases: Schistosomiasis, Trypanosomiasis and Leishmaniasis
Abstract
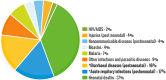
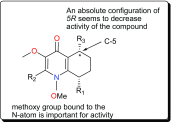
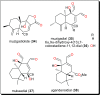
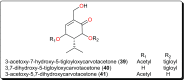
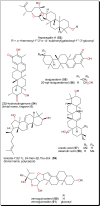
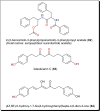
Parasitic diseases continue to represent a threat on a global scale, particularly among the poorest countries in the world. This is particularly because of the absence of vaccines, and in some cases, resistance against available drugs, currently being used for their treatment. In this review emphasis is laid on natural products and scaffolds from African medicinal plants (AMPs) for lead drug discovery and possible further development of drugs for the treatment of parasitic diseases. In the discussion, emphasis has been laid on alkaloids, terpenoids, quinones, flavonoids and narrower compound classes of compounds with micromolar range activities against Schistosoma, Trypanosoma and Leishmania species. In each subparagraph, emphasis is laid on the compound subclasses with most promising in vitro and/or in vivo activities of plant extracts and isolated compounds. Suggestions for future drug development from African medicinal plants have also been provided. This review covering 167 references, including 82 compounds, provides information published within two decades (1997-2017).
Keywords: African medicinal plants; Leishmaniasis; Natural products; Parasitic diseases; Schistosomiasis; Trypanosomiasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



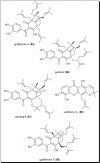
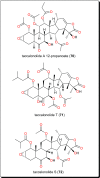

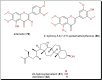
References
-
- Mansueto P, Seidita A, Vitale G, Cascio A. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2014;12:563–581. - PubMed
-
- Wells TN, Alonso PL, Gutteridge WE. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009;8:879–891. - PubMed
-
- Nunes MC, Dones W, Morillo CA, Encina JJ, Ribeiro AL, Council on Chagas Disease of the Interamerican Society of Cardiology J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013;62:767–776. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

