BCL-2 levels do not predict azathioprine treatment response in inflammatory bowel disease, but inhibition induces lymphocyte apoptosis and ameliorates colitis in mice
- PMID: 29745420
- PMCID: PMC6150252
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.13151
BCL-2 levels do not predict azathioprine treatment response in inflammatory bowel disease, but inhibition induces lymphocyte apoptosis and ameliorates colitis in mice
Abstract
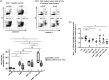
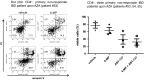
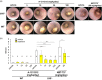
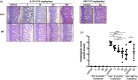
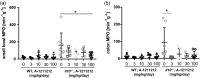
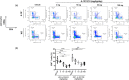
In inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), inflammation is sustained by an exaggerated response of lymphocytes. This results from enhanced expression of anti-apoptotic B cell lymphoma (BCL-2) and BCL-XL associated with a diminished turnover. Azathioprine (AZA) directly targets BCL-2 family-mediated apoptosis. We investigated whether the BCL-2 family expression pattern could be used to predict treatment response to AZA and determined whether BCL-2 inhibitor A-1211212 effectively diminishes lymphocytes and ameliorates inflammation in a model of colitis. BCL-2 family expression pattern was determined by next-generation sequencing (NGS). BCL-2 inhibitor was administered orally to Il10-/- mice. Haematological analyses were performed with an ADVIA 2120 and changes in immune cells were investigated using quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) and fluorescence activated cell sorter (FACS). We determined similar expression levels of BCL-2 family members in patients with remission and patients refractory to treatment, showing that BCL-2 family expression can not predict AZA treatment response. Expression was not correlated with the modified Truelove and Witts activity index (MTWAI). BCL-2 inhibitor initiated cell death in T cells from patients refractory to AZA and reduced lymphocyte count in Il10-/- mice. FACS revealed diminished CD8+ T cells upon BCL-2 inhibitor in Il10-/- mice without influencing platelets. Tnf, Il1β, IfnƔ and Mcp-1 were decreased upon BCL-2 inhibitor. A-1211212 positively altered the colonic mucosa and ameliorated inflammation in mice. Pro-apoptotic BCL-2 inhibitor A-1211212 diminishes lymphocytes and ameliorates colitis in Il10-/- mice without inducing thrombocytopenia. BCL-2 inhibition could be a new therapy option for patients refractory to AZA.
Keywords: A-1211212; ABT-737; BCL-2; BIM; IBD; apoptosis; mucosal T cell turnover.
© 2018 British Society for Immunology.
Figures

References
-
- Ina K, Itoh J, Fukushima K et al Resistance of Crohn’s disease T cells to multiple apoptotic signals is associated with a Bcl‐2/Bax mucosal imbalance. J Immunol 1999;163:1081–90. - PubMed
-
- Mitchell T, Kappler J, Marrack P. Bystander virus infection prolongs activated T cell survival. J Immunol 1999;162:4527–35. - PubMed
-
- Hildeman DA, Zhu Y, Mitchell TC et al Activated T cell death in vivo mediated by proapoptotic bcl‐2 family member bim. Immunity 2002;16:759–67. - PubMed
-
- Boirivant M, Marini M, Di Felice G et al Lamina propria T cells in Crohn’s disease and other gastrointestinal inflammation show defective CD2 pathway‐induced apoptosis. Gastroenterology 1999;116:557–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

