Cofilin Knockdown Attenuates Hemorrhagic Brain Injury-induced Oxidative Stress and Microglial Activation in Mice
- PMID: 29746992
- PMCID: PMC11956763
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.04.036
Cofilin Knockdown Attenuates Hemorrhagic Brain Injury-induced Oxidative Stress and Microglial Activation in Mice
Abstract
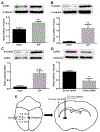
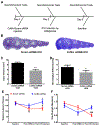
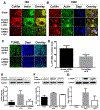
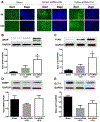
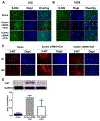
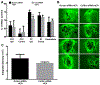
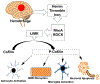
Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) resulting from the rupture of the blood vessels in the brain is associated with significantly higher mortality and morbidity. Clinical studies focused on alleviating the primary injury, hematoma formation and expansion, were largely ineffective, suggesting that secondary injury-induced inflammation and the formation of reactive species also contribute to the overall injury process. In this study, we explored the effects of cofilin knockdown in a mouse model of ICH. Animals given stereotaxic injections of cofilin siRNA, 72-h prior to induction of ICH by collagenase injection within the area of siRNA administration showed significantly decreased cofilin expression levels and lower hemorrhage volume and edema, and the animals performed significantly better in neurobehavioral tasks i.e., rotarod, grip strength and neurologic deficit scores. Cofilin siRNA knocked-down mice had reduced ICH-induced DNA fragmentation, blood-brain barrier disruption and microglial activation, with a concomitant increase in astrocyte activation. Increased expression of pro-survival proteins and decreased markers of oxidative stress were also observed in cofilin siRNA-treated mice possibly due to the reduced levels of cofilin. Our results suggest that cofilin plays a major role in ICH-induced secondary injury, and could become a potential therapeutic target.
Keywords: cofilin; inflammation; intracerebral hemorrhage; microglial activation; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2018 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Adeoye O, Broderick JP (2010) Advances in the management of intracerebral hemorrhage. Nat Rev Neurol 6:593–601. - PubMed
-
- Alhadidi Q, Bin Sayeed MS, Shah ZA (2016) Cofilin as a promising therapeutic target for ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. Transl Stroke Res 7:33–41. - PubMed
-
- Alhadidi Q, Sayeed MS, Shah Z (2017) The interplay between cofilin and phospho-cofilin: its role in maintaining blood brain barrier integrity. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

