CAR T cell therapy for breast cancer: harnessing the tumor milieu to drive T cell activation
- PMID: 29747685
- PMCID: PMC5944113
- DOI: 10.1186/s40425-018-0347-5
CAR T cell therapy for breast cancer: harnessing the tumor milieu to drive T cell activation
Abstract
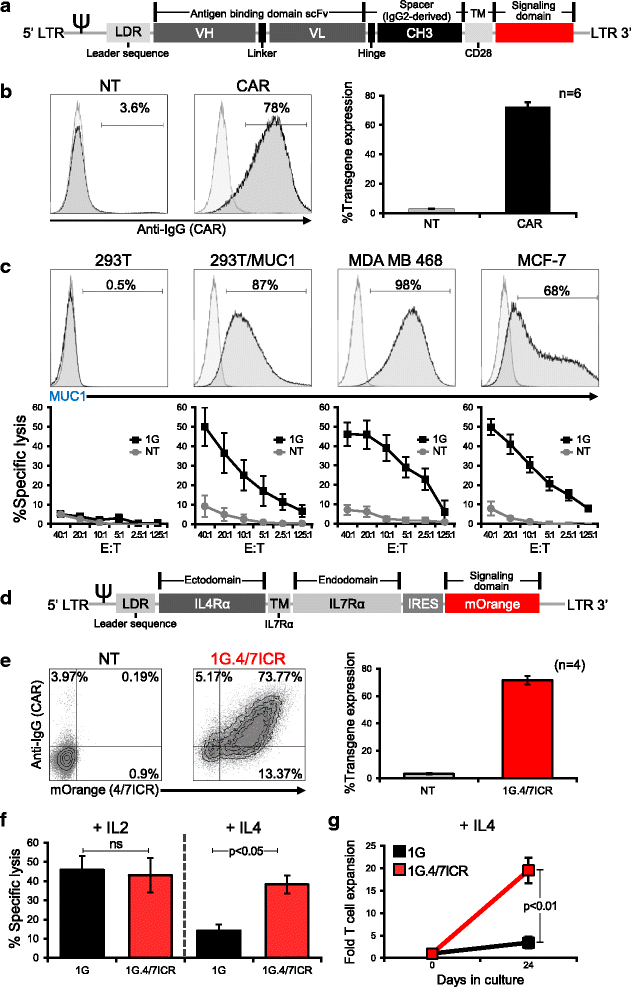
Background: The adoptive transfer of T cells redirected to tumor via chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) has produced clinical benefits for the treatment of hematologic diseases. To extend this approach to breast cancer, we generated CAR T cells directed against mucin1 (MUC1), an aberrantly glycosylated neoantigen that is overexpressed by malignant cells and whose expression has been correlated with poor prognosis. Furthermore, to protect our tumor-targeted cells from the elevated levels of immune-inhibitory cytokines present in the tumor milieu, we co-expressed an inverted cytokine receptor linking the IL4 receptor exodomain with the IL7 receptor endodomain (4/7ICR) in order to transform the suppressive IL4 signal into one that would enhance the anti-tumor effects of our CAR T cells at the tumor site.
Methods: First (1G - CD3ζ) and second generation (2G - 41BB.CD3ζ) MUC1-specific CARs were constructed using the HMFG2 scFv. Following retroviral transduction transgenic expression of the CAR±ICR was assessed by flow cytometry. In vitro CAR/ICR T cell function was measured by assessing cell proliferation and short- and long-term cytotoxic activity using MUC1+ MDA MB 468 cells as targets. In vivo anti-tumor activity was assessed using IL4-producing MDA MB 468 tumor-bearing mice using calipers to assess tumor volume and bioluminescence imaging to track T cells.
Results: In the IL4-rich tumor milieu, 1G CAR.MUC1 T cells failed to expand or kill MUC1+ tumors and while co-expression of the 4/7ICR promoted T cell expansion, in the absence of co-stimulatory signals the outgrowing cells exhibited an exhausted phenotype characterized by PD-1 and TIM3 upregulation and failed to control tumor growth. However, by co-expressing 2G CAR.MUC1 (signal 1 - activation + signal 2 - co-stimulation) and 4/7ICR (signal 3 - cytokine), transgenic T cells selectively expanded at the tumor site and produced potent and durable tumor control in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusions: Our findings demonstrate the feasibility of targeting breast cancer using transgenic T cells equipped to thrive in the suppressive tumor milieu and highlight the importance of providing transgenic T cells with signals that recapitulate physiologic TCR signaling - [activation (signal 1), co-stimulation (signal 2) and cytokine support (signal 3)] - to promote in vivo persistence and memory formation.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Chimeric antigen receptor; Genetic engineering; Inverted cytokine receptor; T cell therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Collection of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were obtained from healthy donors and patients after informed consent on protocols approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) at Baylor College of Medicine (H-15152). Mice were housed and treated in accordance with Baylor College of Medicine Animal Husbandry and Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee guidelines (AN-5639).
Competing interests
The Center for Cell and Gene Therapy at Baylor College of Medicine established a collaboration with Celgene at the time the work was conducted. S.S., A.M.L., and J.F.V. have filed a related patent application.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures




References
-
- Brentjens RJ, Davila ML, Riviere I, Park J, Wang X, Cowell LG, Bartido S, Stefanski J, Taylor C, Olszewska M, et al. CD19-targeted T cells rapidly induce molecular remissions in adults with chemotherapy-refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Sci Transl Med. 2013;5(177):177ra38. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3005930. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
