Proteomic profiling identifies key coactivators utilized by mutant ERα proteins as potential new therapeutic targets
- PMID: 29748621
- PMCID: PMC6095836
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-018-0284-2
Proteomic profiling identifies key coactivators utilized by mutant ERα proteins as potential new therapeutic targets
Abstract
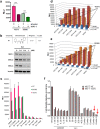
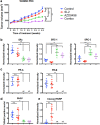
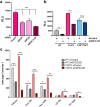
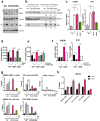
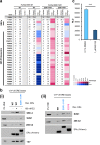
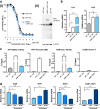
Approximately 75% of breast cancers are estrogen receptor alpha (ERα)-positive and are treatable with endocrine therapies, but often patients develop lethal resistant disease. Frequent mutations (10-40%) in the ligand-binding domain (LBD) codons in the gene encoding ERα (ESR1) have been identified, resulting in ligand-independent, constitutively active receptors. In addition, ESR1 chromosomal translocations can occur, resulting in fusion proteins that lack the LBD and are entirely unresponsive to all endocrine treatments. Thus, identifying coactivators that bind to these mutant ERα proteins may offer new therapeutic targets for endocrine-resistant cancer. To define coactivator candidate targets, a proteomics approach was performed profiling proteins recruited to the two most common ERα LBD mutants, Y537S and D538G, and an ESR1-YAP1 fusion protein. These mutants displayed enhanced coactivator interactions as compared to unliganded wild-type ERα. Inhibition of these coactivators decreased the ability of ESR1 mutants to activate transcription and promote breast cancer growth in vitro and in vivo. Thus, we have identified specific coactivators that may be useful as targets for endocrine-resistant breast cancers.
Conflict of interest statement
B.W.O., D.M.L., J.W., A.D.R., Y.Y., and C.E.F. disclose an equity position in Coactigon, Inc.; M.J.E. received a consulting fee from AstraZeneca.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA178765/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA213535/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA207270/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD007857/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK071900/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD008188/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA125123/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056338/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F31 CA210385/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM115622/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA207701/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA072038/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM088129/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

