Evaluation of interleukin-6 and its soluble receptor components sIL-6R and sgp130 as markers of inflammation in inflammatory bowel diseases
- PMID: 29748708
- PMCID: PMC6002455
- DOI: 10.1007/s00384-018-3069-8
Evaluation of interleukin-6 and its soluble receptor components sIL-6R and sgp130 as markers of inflammation in inflammatory bowel diseases
Abstract
Purpose: Interleukin-6 (IL-6) production and signalling are increased in the inflamed mucosa in inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD). As published serum levels of IL-6 and its soluble receptors sIL-6R and sgp130 in IBD are from small cohorts and partly contradictory, we systematically evaluated IL-6, sIL-6R and sgp130 levels as markers of disease activity in Crohn's disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC).
Methods: Consecutive adult outpatients with confirmed CD or UC were included, and their disease activity and medication were monitored. Serum from 212 CD patients (815 measurements) and 166 UC patients (514 measurements) was analysed, and 100 age-matched healthy blood donors were used as controls.
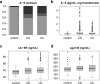
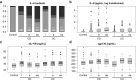
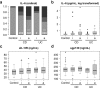
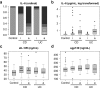
Results: IL-6 serum levels were significantly elevated in active versus inactive CD and UC, also compared with healthy controls. However, only a fraction of IBD patients showed increased serum IL-6. IL-6 levels ranged up to 32.7 ng/mL in active CD (> 5000-fold higher than in controls), but also up to 6.9 ng/mL in inactive CD. Increases in active UC (up to 195 pg/mL) and inactive UC (up to 27 pg/mL) were less pronounced. Associations between IL-6 serum levels and C-reactive protein concentrations as well as leukocyte and thrombocyte counts were observed. Median sIL-6R and sgp130 levels were only increased by up to 15%, which was considered of no diagnostic significance.
Conclusions: Only a minority of IBD patients shows elevated IL-6 serum levels. However, in these patients, IL-6 is strongly associated with disease activity. Its soluble receptors sIL-6R and sgp130 do not appear useful as biomarkers in IBD.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Crohn’s disease; Inflammatory bowel diseases; Interleukin-6; Ulcerative colitis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
GHW and DS are employed by CONARIS Research Institute AG, which has out-licenced its interleukin-6 inhibitor olamkicept to Ferring Pharmaceuticals. UL, BBR and TMR are employed by Ferring Pharmaceuticals. SSc heads the supervisory board of CONARIS. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Ethics approval was granted by the ethics committee of the medical faculty of Kiel University prior to the study (AZ D489/14). All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. The ethical concept of healthcare-embedded biobanking with broad informed consents as implemented in Kiel has recently been described [35].
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

