Two-photon probes for in vivo multicolor microscopy of the structure and signals of brain cells
- PMID: 29748872
- PMCID: PMC6119111
- DOI: 10.1007/s00429-018-1678-1
Two-photon probes for in vivo multicolor microscopy of the structure and signals of brain cells
Abstract
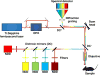
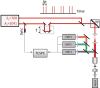
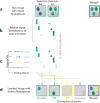
Imaging the brain of living laboratory animals at a microscopic scale can be achieved by two-photon microscopy thanks to the high penetrability and low phototoxicity of the excitation wavelengths used. However, knowledge of the two-photon spectral properties of the myriad fluorescent probes is generally scarce and, for many, non-existent. In addition, the use of different measurement units in published reports further hinders the design of a comprehensive imaging experiment. In this review, we compile and homogenize the two-photon spectral properties of 280 fluorescent probes. We provide practical data, including the wavelengths for optimal two-photon excitation, the peak values of two-photon action cross section or molecular brightness, and the emission ranges. Beyond the spectroscopic description of these fluorophores, we discuss their binding to biological targets. This specificity allows in vivo imaging of cells, their processes, and even organelles and other subcellular structures in the brain. In addition to probes that monitor endogenous cell metabolism, studies of healthy and diseased brain benefit from the specific binding of certain probes to pathology-specific features, ranging from amyloid-β plaques to the autofluorescence of certain antibiotics. A special focus is placed on functional in vivo imaging using two-photon probes that sense specific ions or membrane potential, and that may be combined with optogenetic actuators. Being closely linked to their use, we examine the different routes of intravital delivery of these fluorescent probes according to the target. Finally, we discuss different approaches, strategies, and prerequisites for two-photon multicolor experiments in the brains of living laboratory animals.
Keywords: Calcium imaging; Electroporation; Functional imaging; Intravital; Multicolor microscopy; Two-photon cross section.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
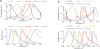
Similar articles
-
Multicolor three-photon fluorescence imaging with single-wavelength excitation deep in mouse brain.Sci Adv. 2021 Mar 17;7(12):eabf3531. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abf3531. Print 2021 Mar. Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 33731355 Free PMC article.
-
Visible-wavelength two-photon excitation microscopy for fluorescent protein imaging.J Biomed Opt. 2015 Oct;20(10):101202. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.20.10.101202. J Biomed Opt. 2015. PMID: 26238663
-
Fluorene-based fluorescent probes with high two-photon action cross-sections for biological multiphoton imaging applications.J Biomed Opt. 2005 Sep-Oct;10(5):051402. doi: 10.1117/1.2104528. J Biomed Opt. 2005. PMID: 16292939
-
Voltage imaging with ANNINE dyes and two-photon microscopy of Purkinje dendrites in awake mice.Neurosci Res. 2020 Mar;152:15-24. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2019.11.007. Epub 2019 Nov 20. Neurosci Res. 2020. PMID: 31758973 Review.
-
Molecular engineering of two-photon fluorescent probes for bioimaging applications.Methods Appl Fluoresc. 2017 Mar 22;5(1):012003. doi: 10.1088/2050-6120/aa61b0. Methods Appl Fluoresc. 2017. PMID: 28328541 Review.
Cited by
-
Robust blind spectral unmixing for fluorescence microscopy using unsupervised learning.PLoS One. 2019 Dec 2;14(12):e0225410. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225410. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31790435 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody-based in vivo leukocyte label for two-photon brain imaging in mice.Neurophotonics. 2022 Jul;9(3):031917. doi: 10.1117/1.NPh.9.3.031917. Epub 2022 May 24. Neurophotonics. 2022. PMID: 35637871 Free PMC article.
-
CoSiDeX: A hyperspectral fluorescent protein resource for highly multiplexed imaging.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 14:2025.05.09.652935. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.09.652935. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40463276 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Genetically encoded fluorescent sensors for imaging neuronal dynamics in vivo.J Neurochem. 2023 Feb;164(3):284-308. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15608. Epub 2022 Apr 9. J Neurochem. 2023. PMID: 35285522 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two-photon excitation fluorescent spectral and decay properties of retrograde neuronal tracer Fluoro-Gold.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 10;11(1):18053. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-97562-3. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34508127 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

