Colonoscopic decompression of childhood sigmoid and cecal volvulus
- PMID: 29749331
- PMCID: PMC6284711
- DOI: 10.5152/tjg.2018.17507
Colonoscopic decompression of childhood sigmoid and cecal volvulus
Abstract
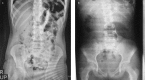
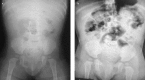
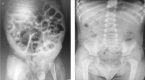
Cases of colonic volvulus in children are infrequently described in the literature. Here we describe the case of three patients with colonic volvulus. The first patient was a 10-year-old girl with abdominal dilation and pain and no bowel movement for 48 h. Her abdominal X-ray showed the coffee bean sign adjacent to the diaphragm, which was compatible with a diagnosis of cecal volvulus. The second patient was a 4-year-old boy with a history of chronic constipation during the past year and with no bowel movement for 24 h. Clinical manifestations included severe nausea, vomiting, and abdominal distension. His abdominal X-ray demonstrated the coffee bean sign in the right upper quadrant with upward convexity corresponding to a diagnosis of sigmoid volvulus. The third patient was a 10-month-old male who presented with excessive crying, malnutrition, and no bowel movement for 36 h. His abdominal X-ray demonstrated the coffee bean sign in the left upper quadrant with upward convexity. The presence of gas was not observed in the distal obstructed region, corresponding to a diagnosis of sigmoid volvulus. All three patients successfully underwent colonoscopy for volvulus reduction. Volvulus did not reoccur in any of the patients within 6 months of follow-up. It is recommended to perform abdominal X-ray imaging in patients who present with abdominal pain and distension, diarrhea, or constipation for possibly diagnosing volvulus.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Tannouri S, Hendi A, Gilje E, Grissom L, Katz D. Pediatric colonic volvulus: A single-institution experience and review. J Pediatr Surg. 2017;52:1062–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2017.01.063 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Khalayleh H, Koplewitz BZ, Kapuller V, Armon Y, Abu-Leil S, Arbell D. Neonatal sigmoid volvulus. J Pediatr Surg. 2016;51:1782–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2016.06.017 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shah SS, Louie JP, Fein JA. Cecal volvulus in childhood. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2002;18:300–2. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006565-200208000-00016 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Salas S, Angel CA, Salas N, Murillo C, Swischuk L. Sigmoid volvulus in children and adolescents. J Am Coll Surg. 2000;190:717–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1072-7515(00)00270-2 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Erdogan D, Karaman A, Cavusoglu YH, Karaman I, Ozcatal M. Colon Volvulus in Childhood: Case Report. Turkiye Klinikleri J Med Sci. 2012;32:1131–4. https://doi.org/10.5336/medsci.2010-19065 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
