Immunotherapy by targeting of VGKC complex for seizure control and prevention of cognitive impairment in a mouse model of epilepsy
- PMID: 29749462
- PMCID: PMC6059666
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9004
Immunotherapy by targeting of VGKC complex for seizure control and prevention of cognitive impairment in a mouse model of epilepsy
Abstract
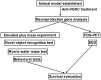
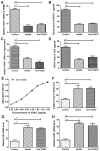
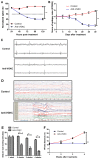
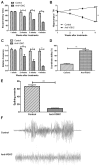
Epilepsy is a type of refractory neurologic disorder mental disease, which is associated with cognitive impairments and memory dysfunction. However, the potential mechanisms of epilepsy are not well understood. Previous evidence has identified the voltage gated potassium channel complex (VGKC) as a target in various cohorts of patients with epilepsy. In the present study, the efficacy of an antibody against VGKC (anti‑VGKC) for the treatment of epilepsy in mice was investigated. A mouse model of lithium‑pilocarpine temporal lobe epilepsy was established and anti‑VGKC treatment was administered for 30 days. Memory impairment, anxiety, visual attention, inhibitory control and neuronal loss were measured in the mouse model of lithium‑pilocarpine temporal lobe epilepsy. The results revealed that epileptic mice treated with anti‑VGKC were able to learn the task and presented attention impairment, even a tendency toward impulsivity and compulsivity. It was also exhibited that anti‑VGKC treatment decreased neuronal loss in structures classically associated with attentional performance in hippocampus. Mice who received Anti‑VGKC treatment had inhibited motor seizures and hippocampal damage as compared with control mice. In conclusion, these results indicated that anti‑VGKC treatment may present benefits for improvements of the condition of motor attention impairment and cognitive competence, which suggests that VGKC may be a potential target for the treatment of epilepsy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Attention and executive functions in a rat model of chronic epilepsy.Epilepsia. 2014 May;55(5):644-653. doi: 10.1111/epi.12549. Epub 2014 Feb 22. Epilepsia. 2014. PMID: 24621352
-
VGKC complex antibodies in epilepsy: diagnostic yield and therapeutic implications.Seizure. 2013 Nov;22(9):776-9. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2013.06.004. Epub 2013 Jul 7. Seizure. 2013. PMID: 23838087
-
The frequency of spontaneous seizures in rats correlates with alterations in sensorimotor gating, spatial working memory, and parvalbumin expression throughout limbic regions.Neuroscience. 2016 Jan 15;312:86-98. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.11.008. Epub 2015 Nov 12. Neuroscience. 2016. PMID: 26582750
-
Voltage-gated potassium channel-associated limbic encephalitis in the West of Scotland: case reports and literature review.Scott Med J. 2009 Nov;54(4):27-31. doi: 10.1258/rsmsmj.54.4.27. Scott Med J. 2009. PMID: 20034278 Review.
-
[Autoimmune Associated Encephalitis and Dementia].Brain Nerve. 2016 Apr;68(4):341-50. doi: 10.11477/mf.1416200403. Brain Nerve. 2016. PMID: 27056852 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Scoping review of disease-modifying effect of drugs in experimental epilepsy.Front Neurol. 2023 Feb 23;14:1097473. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1097473. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36908628 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of key potassium channel genes of temporal lobe epilepsy by bioinformatics analyses and experimental verification.Front Neurol. 2023 Jul 7;14:1175007. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1175007. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37483435 Free PMC article.
-
Autoimmune Epilepsy - Novel Multidisciplinary Analysis, Discoveries and Insights.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 12;12:762743. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.762743. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35095841 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

