Placental protein 14 as a potential biomarker for diagnosis of preterm premature rupture of membranes
- PMID: 29749501
- PMCID: PMC6059659
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8967
Placental protein 14 as a potential biomarker for diagnosis of preterm premature rupture of membranes
Abstract
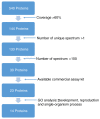
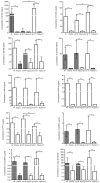
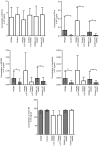
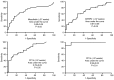
Premature rupture of membranes (PROM) is a common pregnancy complication that frequently results in maternal and perinatal morbidity. The present methods for diagnosing PROM do not satisfy clinical requirements. The present study aimed to examine the proteome profile of amniotic fluid (AF) and maternal plasma, screen unique proteins in AF, and evaluate their diagnostic value for diagnosing PROM. The proteome profiles of AF and maternal plasma were examined via liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry‑based proteomic techniques. The protein expression levels of diagnostic candidates in AF, maternal plasma and vaginal fluid were determined by ELISA analysis and Magnetic Luminex® screening assays. The diagnostic value of potential biomarkers was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic curves. A lateral flow assay was developed based on colloidal gold immunochromatography technology. The present study identified 540 unique proteins in AF, 12 of which were chosen for further detection. The present results demonstrated that expression levels of pulmonary surfactant‑associated protein B, BPI fold‑containing family A member 1, zymogen granule protein 16 homolog B, EGF‑containing fibulin‑like extracellular matrix protein 1, keratin, type II cytoskeletal 4, keratin, type I cytoskeletal 19, placental protein 14 (PP14), insulin‑like growth factor‑binding protein 2, mesothelin and serpin family B member 3 were significantly higher in AF compared with in maternal plasma (P<0.01). Furthermore, PP14 was observed to have excellent diagnostic accuracy for preterm PROM (PPROM), with a respective sensitivity and specificity of 100 and 87.5% when the cutoff value was 0.008 µg/ml. The PP14‑based lateral flow assay demonstrated a visual detection threshold of 0.008 µg/ml. The results from the present study suggested that PP14 may be a novel potential biomarker for PPROM, and may be developed into a lateral flow assay for bedside application to rapidly diagnose PPROM.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Non-invasively collected amniotic fluid as a source of possible biomarkers for premature rupture of membranes investigated by proteomic approach.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2014 Feb;289(2):299-306. doi: 10.1007/s00404-013-2967-9. Epub 2013 Jul 20. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2014. PMID: 23872981
-
Maternal plasma procalcitonin concentrations in pregnancy complicated by preterm premature rupture of membranes.Mediators Inflamm. 2007;2007:35782. doi: 10.1155/2007/35782. Mediators Inflamm. 2007. PMID: 17710246 Free PMC article.
-
Premature preterm rupture of the membrane diagnosis in early pregnancy: PAMG-1 and IGFBP-1 detection in amniotic fluid with biochemical tests.Clin Biochem. 2013 Dec;46(18):1816-9. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2013.10.006. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Clin Biochem. 2013. PMID: 24140132
-
Coagulation and fibrinolysis in amniotic fluid: physiology and observations on amniotic fluid embolism, preterm fetal membrane rupture, and pre-eclampsia.Semin Thromb Hemost. 2011 Mar;37(2):165-74. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1270345. Epub 2011 Mar 2. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2011. PMID: 21370219 Review.
-
Are biological markers relevant for the diagnosis and the prognosis of preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM)?Clin Chem Lab Med. 2012 Apr 14;50(6):1015-9. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2011-1850. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2012. PMID: 22706240 Review.
Cited by
-
The abundances of LTF and SOD2 in amniotic fluid are potential biomarkers of gestational age and preterm birth.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 25;13(1):4903. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-31486-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36966172 Free PMC article.
-
IgGFc-binding protein in pregnancies complicated by spontaneous preterm delivery: a retrospective cohort study.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 17;11(1):6107. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85473-2. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33731725 Free PMC article.
-
Current and Emerging Strategies for Prediction and Diagnosis of Prelabour Rupture of the Membranes: A Narrative Review.Malays J Med Sci. 2021 Jun;28(3):5-17. doi: 10.21315/mjms2021.28.3.2. Epub 2021 Jun 30. Malays J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34285641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Serum Biomarkers Associated with Premature Rupture of Fetal Membranes in the First Trimester.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 8;13:915935. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.915935. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35873552 Free PMC article.
-
Keratin 8 Is an Inflammation-Induced and Prognosis-Related Marker for Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma.Dis Markers. 2022 Jul 27;2022:8159537. doi: 10.1155/2022/8159537. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 35958278 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jiang HL, Wang X, Zhang WY. Investigation of premature rupture of membrane in Beijing area. Chin J Clin. 2015:74–76. (In Chinese)
-
- Medina TM, Hill DA. Preterm premature rupture of membranes: Diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician. 2006;73:659–664. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

