Secondary Hypogammaglobulinemia After Rituximab for Neuromyelitis Optica: A Case Report
- PMID: 29752554
- PMCID: PMC5948191
- DOI: 10.1007/s40800-018-0087-y
Secondary Hypogammaglobulinemia After Rituximab for Neuromyelitis Optica: A Case Report
Abstract
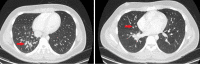
A 17-year-old male with history of neuromyelitis optica and seizures presented to the pulmonology clinic for evaluation of recurrent pneumonias. He had received rituximab for the past 6 years. Over the past 2 years, he experienced four episodes of pneumonia. In between these episodes, he would improve briefly but continued to have daily cough that was productive with yellow phlegm. He also had recurrent rhinitis and sinusitis despite multiple antibiotic courses. Review of chest X-rays revealed localized right middle lobe and right lower lobe infiltrates. An extensive workup was performed, including computed tomography (CT) of the chest and bronchoscopy to rule out congenital lesions of the right lung and foreign body aspiration. Chest CT showed right lower lobe bronchiectasis. Flexible bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage showed normal anatomy with thick mucus secretions in the right lower lobe. Immunologic evaluation was performed and revealed low levels of immunoglobulin (Ig)-G, IgM, and IgA, which had declined since initiation of rituximab. Lymphocyte subset testing was remarkable for low cluster of differentiation (CD)-19. He was referred to allergy and immunology and was initiated on immunoglobulin-replacement therapy (IGRT) for acquired hypogammaglobulinemia secondary to rituximab. There was marked clinical improvement after initiation of IGRT.
Conflict of interest statement
Consent for Publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for the publication of this case report and the accompanying images. A copy of the written consent may be requested for review from the corresponding author.
Conflict of interest
Lara Farhat, Jasmeen Dara, Susan Duberstein, and Aliva De have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Evangelopoulos ME, Andreadou E, Koutsis G, Koutoulidis V, Anagnostouli M, Katsika P, Evangelopuols DS, Evdokimidis I, Kilidireas C. Treatment of neuromyelitis optica and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders with rituximab using a maintenance treatment regimen and close CD19 B cell monitoring. A six-year follow-up. J Neurol Sci. 2017;372:92–96. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2016.11.016. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pellkofer HL, Krumbholz M, Berthele A, Hemmer B, Gerdes LA, Havla J, Bittner R, Canis M, Meinl E, Hohlfeld R, Kuempfel T. Long-term follow up of patients with neuromyelitis optica after repeated therapy with rituximab. Neurology. 2011;76(15):1310–1315. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182152881. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous