A Genetically Encoded Biosensor Reveals Location Bias of Opioid Drug Action
- PMID: 29754753
- PMCID: PMC6481295
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.04.021
A Genetically Encoded Biosensor Reveals Location Bias of Opioid Drug Action
Abstract
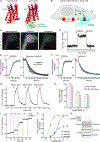
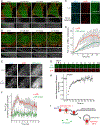
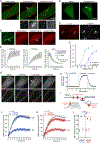
Opioid receptors (ORs) precisely modulate behavior when activated by native peptide ligands but distort behaviors to produce pathology when activated by non-peptide drugs. A fundamental question is how drugs differ from peptides in their actions on target neurons. Here, we show that drugs differ in the subcellular location at which they activate ORs. We develop a genetically encoded biosensor that directly detects ligand-induced activation of ORs and uncover a real-time map of the spatiotemporal organization of OR activation in living neurons. Peptide agonists produce a characteristic activation pattern initiated in the plasma membrane and propagating to endosomes after receptor internalization. Drugs produce a different activation pattern by additionally driving OR activation in the somatic Golgi apparatus and Golgi elements extending throughout the dendritic arbor. These results establish an approach to probe the cellular basis of neuromodulation and reveal that drugs distort the spatiotemporal landscape of neuronal OR activation.
Keywords: GPCR; Golgi; biosensor; endosome; ligand bias; ligand-induced activation; opioid drug; opioid receptor; signaling; subcellular location.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Comment in
-
A pathway less travelled.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2018 Jul;19(7):389. doi: 10.1038/s41583-018-0025-0. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29872219 No abstract available.
-
Beware of Undertow: Opioid Drugs Generate Additional Waves of Intracellular Signaling.Neuron. 2018 Jun 6;98(5):870-872. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.05.035. Neuron. 2018. PMID: 29879387 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arttamangkul S, Alvarez-Maubecin V, Thomas G, Williams JT, and Grandy DK (2000). Binding and internalization of fluorescent opioid peptide conjugates in living cells. Mol. Pharmacol 58, 1570–1580. - PubMed
-
- Bradbury AF, Smyth DG, and Snell CR (1976). Biosynthetic origin and receptor conformation of methionine enkephalin. Nature 260, 165–166. - PubMed
-
- Calebiro D, Nikolaev VO, Persani L, and Lohse MJ (2010). Signaling by internalized Gprotein-coupled receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci 31, 221–228. - PubMed

