Evaluation of Silibinin Effects on the Viability of HepG2 (Human hepatocellular liver carcinoma) and HUVEC (Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial) Cell Lines
- PMID: 29755557
- PMCID: PMC5937096
Evaluation of Silibinin Effects on the Viability of HepG2 (Human hepatocellular liver carcinoma) and HUVEC (Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial) Cell Lines
Abstract
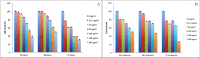
Human hepatocellular carcinoma is one of the most common recurrent malignancies since there is no effective therapy for it. Silibinin, a widely used drug and supplement for various liver disorders, demonstrated anti-cancer effects on human hepatocellular carcinoma, human prostate adenocarcinoma cells, human breast carcinoma cells, human ectocervical carcinoma cells, and human colon cancer cells. Considering the anti-hepatotoxic activity of silibinin and its strong preventive and anti-cancer efficacy against various epithelial cancers, we investigated the efficacy of silibinin against human HCC and HUVEC cell lines. Silibinin effects on the growth and mode of cell death of these two cell lines are presented in this paper. HepG2 and HUVEC cells were incubated with different doses of silibinin (12.5, 25, 50, 100, 150 and 200 μg/mL) at 24, 48, and 72 h. Cytotoxicity was assessed using MTT and Trypan blue assays. Mode of cell death induced by silibinin was investigated using LDH assay and acridine orange/PI double dye staining. The results showed that silibinin has dose-dependent inhibitory effect on the viability of HepG2 and HUVEC cells. However, Silibinin causes a more continuous dose-dependent cytotoxicity in HepG2 cells compared to the HUVEC cells in which some degrees of resistance is apparent at the beginning. The mode of cell death looks also different in these two cell lines with HepG2 cells being more in favor of apoptosis while necrosis is more evident for the HUVEC cells.
Keywords: HUVEC; HepG2; Human hepatocellular carcinoma; Silibinin.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Silibinin efficacy against human hepatocellular carcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Dec 1;11(23):8441-8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1646. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16322307
-
Combined treatment with silibinin and either sorafenib or gefitinib enhances their growth-inhibiting effects in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2015 Mar;21(1):49-59. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2015.21.1.49. Epub 2015 Mar 25. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25834802 Free PMC article.
-
Antiproliferative and apoptotic effects of silibinin in rat prostate cancer cells.Prostate. 2002 Nov 1;53(3):211-7. doi: 10.1002/pros.10146. Prostate. 2002. PMID: 12386921
-
Silibinin strongly inhibits growth and survival of human endothelial cells via cell cycle arrest and downregulation of survivin, Akt and NF-kappaB: implications for angioprevention and antiangiogenic therapy.Oncogene. 2005 Feb 10;24(7):1188-202. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208276. Oncogene. 2005. PMID: 15558015
-
Silibinin: an old drug for hematological disorders.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 11;8(51):89307-89314. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19153. eCollection 2017 Oct 24. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29179521 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Zebularine on p16INK4a, p14ARF, p15INK4b, and DNA Methyltransferase 1 Gene Expression, Cell Growth Inhibition, and Apoptosis Induction in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma PLC/PRF5 and Pancreatic Cancer PA-TU-8902 Cell Lines.Iran J Pharm Res. 2020 Fall;19(4):193-202. doi: 10.22037/ijpr.2020.112223.13614. Iran J Pharm Res. 2020. PMID: 33841535 Free PMC article.
-
A New Glucosyl Flavone with Inhibitory Activity of Cancer Cell Viability and Other Bioactive Constituents from the Traditional Kurdish Plant Plantago loeflingii L.Molecules. 2024 Feb 29;29(5):1079. doi: 10.3390/molecules29051079. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38474591 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive evaluation of the therapeutic potential of silibinin: a ray of hope in cancer treatment.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 29;15:1349745. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1349745. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38487172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vitro Cytotoxicity of Reproductive Stage Withania somnifera Leaf and Stem on HepG2 Cell Line.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Dec 26;2023:8832166. doi: 10.1155/2023/8832166. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 38169931 Free PMC article.
-
Silibinin down-regulates PD-L1 expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by interfering with tumor cell glycolytic metabolism.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020 Sep 15;690:108479. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2020.108479. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020. PMID: 32679194 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Entezari M, Mokhtari MJ, Hashemi M. Evaluation of Silibinin on the Viability of MCF-7 Human Breast Adenocarcinoma and HUVEC (Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial) cell lines. Advanced Studies in Biol. 2011;6:283–88.
-
- Jemal A, Murray T, Ward E, Samuels A, TiwariRC , GhafoorA , FeuerE , Thun MJ. Cancer statistics. CA: Cancer J. Clin. 2005;55:10–30. - PubMed
-
- Ghasemian A, Mehrabian S, Majd A. Peel Extracts of two Iranian cultivars of Pomegranate (punicagranatum) have antioxidant and antimutagenic activities. Pakistan. J. Biol. Sci. 2006;7:1402–5.
-
- Sporn MB, Suh N. Chemoprevention of Cancer. Carcinogen. 2000;21:525–30. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal R. Cell Signaling and Regulators of Cell Cycle as Molecular Targets for Prostate Cancer Prevention by Dietary Agents. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000;60:1051–59. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
