Vitamin D deficiency and degree of coronary artery luminal stenosis in women undergoing coronary angiography: a prospective observational study
- PMID: 29755836
- PMCID: PMC5944811
Vitamin D deficiency and degree of coronary artery luminal stenosis in women undergoing coronary angiography: a prospective observational study
Abstract
Background and aims: Low serum 25-OH D levels are associated with increased cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Recent studies have linked 25-OH D deficiency with the presence of CAD. Women, especially post-menopausal, tend to suffer from accelerated atherosclerosis, along with vitamin D deficiency. In the present study we sought to investigate whether there is a direct association of coronary artery luminal stenosis with 25-OH D deficiency in women.
Patients and methods: We enrolled women aged >40 who were scheduled to undergo elective coronary angiography between 3/2011 and 10/2016 in a prospective observational study.
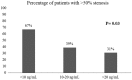
Results: We included a total of 105 women. Patients had hypertension (73%), hyperlipidemia (54%), diabetes (29%), smoking (31%), family history of CAD (62%), and known CAD (21%). Median 25-OH D levels were 15.8 ng/mL (range, 3.9-79). Patients had left-anterior descending (31%), left circumflex (22%), and right coronary artery disease (26%); 27% had 2-vessel and 11% had 3-vessel disease. There was a significant inverse correlation between 25-OH D levels and the degree of maximum luminal stenosis. The burden of CAD increased across categories of worsening 25-OH D deficiency.
Conclusions: Vitamin D deficiency is associated with the degree of luminal stenosis and burden of CAD in women undergoing coronary angiography. Future studies should investigate if the repletion of 25-OH D impacts the progression of CAD and cardiovascular mortality.
Keywords: 25-OH D; coronary artery disease; vitamin D; women.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Dobnig H, Pilz S, Scharnagl H, Renner W, Seelhorst U, Wellnitz B, Kinkeldei J, Boehm BO, Weihrauch G, Maerz W. Independent association of low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin d and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin d levels with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. Arch Intern Med. 2008;168:1340–1349. - PubMed
-
- Kilkkinen A, Knekt P, Aro A, Rissanen H, Marniemi J, Heliovaara M, Impivaara O, Reunanen A. Vitamin D status and the risk of cardiovascular disease death. Am J Epidemiol. 2009;170:1032–1039. - PubMed
-
- Chowdhury R, Kunutsor S, Vitezova A, Oliver-Williams C, Chowdhury S, Kiefte-de-Jong JC, Khan H, Baena CP, Prabhakaran D, Hoshen MB, Feldman BS, Pan A, Johnson L, Crowe F, Hu FB, Franco OH. Vitamin D and risk of cause specific death: systematic review and meta-analysis of observational cohort and randomised intervention studies. BMJ. 2014;348:g1903. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous