Isolated Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome in identical twins
- PMID: 29755940
- PMCID: PMC5944030
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hrcr.2018.01.013
Isolated Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome in identical twins
Keywords: Catheter ablation; Identical twins; Monozygotic twin; Supraventricular tachycardia; Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.
Figures
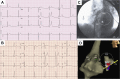
References
-
- Gollob M.H., Green M.S., Tang A.S. Identification of a gene responsible for familial Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1823–1831. - PubMed
-
- Ehtisham J., Watkins H. Is Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome a genetic disease? J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2005;16:1258–1262. - PubMed
-
- Richards S., Aziz N., Bale S., ACMG Laboratory Quality Assurance Committee Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. 2015;17:405–424. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Scheinman M.M. Familial preexcitation and pseudo-preexcitation syndromes. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2006;17:733–734. - PubMed
-
- Schneider R.G. Familial occurrence of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Am Heart J. 1969;78:34–37. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

