Modulation of H-NS transcriptional silencing by magnesium
- PMID: 29757411
- PMCID: PMC6009595
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gky387
Modulation of H-NS transcriptional silencing by magnesium
Abstract
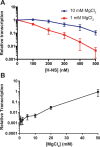
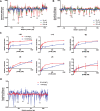
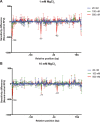
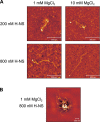
The bacterial histone-like protein H-NS silences AT-rich DNA, binding DNA as 'stiffened' filaments or 'bridged' intrastrand loops. The switch between these modes has been suggested to depend on the concentration of divalent cations, in particular Mg2+, with elevated Mg2+ concentrations associated with a transition to bridging. Here we demonstrate that the observed binding mode is a function of the local concentration of H-NS and its cognate binding sites, as well as the affinity of the interactions between them. Mg2+ does not control a binary switch between these two modes but rather modulates the affinity of this interaction, inhibiting the DNA-binding and silencing activity of H-NS in a continuous linear fashion. The direct relationship between conditions that favor stiffening and transcriptional silencing activity suggests that although both modes can occur in the cell, stiffening is the predominant mode of binding at silenced genes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A divalent switch drives H-NS/DNA-binding conformations between stiffening and bridging modes.Genes Dev. 2010 Feb 15;24(4):339-44. doi: 10.1101/gad.1883510. Genes Dev. 2010. PMID: 20159954 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Salt Valency in the Switch of H-NS Proteins between DNA-Bridging and DNA-Stiffening Modes.Biophys J. 2018 May 22;114(10):2317-2325. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2018.02.030. Epub 2018 Mar 23. Biophys J. 2018. PMID: 29576193 Free PMC article.
-
H-NS cooperative binding to high-affinity sites in a regulatory element results in transcriptional silencing.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007 May;14(5):441-8. doi: 10.1038/nsmb1233. Epub 2007 Apr 15. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17435766
-
H-NS and RNA polymerase: a love-hate relationship?Curr Opin Microbiol. 2015 Apr;24:53-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2015.01.009. Epub 2015 Jan 30. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25638302 Review.
-
Xenogeneic Silencing and Its Impact on Bacterial Genomes.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2016 Sep 8;70:199-213. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-102215-095301. Epub 2016 Jun 17. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27359215 Review.
Cited by
-
Bacterial H-NS contacts DNA at the same irregularly spaced sites in both bridged and hemi-sequestered linear filaments.iScience. 2022 May 18;25(6):104429. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104429. eCollection 2022 Jun 17. iScience. 2022. PMID: 35669520 Free PMC article.
-
Multifactorial genetic control and magnesium levels govern the production of a Streptomyces antibiotic with unusual cell density dependence.mSystems. 2024 Apr 16;9(4):e0136823. doi: 10.1128/msystems.01368-23. Epub 2024 Mar 11. mSystems. 2024. PMID: 38493407 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing cryptic specialized metabolism in Streptomyces by the nucleoid-associated protein Lsr2.Elife. 2019 Jun 19;8:e47691. doi: 10.7554/eLife.47691. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31215866 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuation of a DNA cruciform by a conserved regulator directs T3SS1 mediated virulence in Vibrio parahaemolyticus.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jul 7;51(12):6156-6171. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad370. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37158250 Free PMC article.
-
Hypothesis: nucleoid-associated proteins segregate with a parental DNA strand to generate coherent phenotypic diversity.Theory Biosci. 2021 Feb;140(1):17-25. doi: 10.1007/s12064-020-00323-5. Epub 2020 Oct 23. Theory Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33095418
References
-
- Navarre W.W., Porwollik S., Wang Y., McClelland M., Rosen H., Libby S.J., Fang F.C.. Selective silencing of foreign DNA with low GC content by the H-NS protein in Salmonella. Science. 2006; 313:236–238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

