Pathogenesis of Keratoconus: The intriguing therapeutic potential of Prolactin-inducible protein
- PMID: 29758268
- PMCID: PMC6235698
- DOI: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2018.05.002
Pathogenesis of Keratoconus: The intriguing therapeutic potential of Prolactin-inducible protein
Abstract
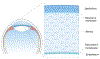
Keratoconus (KC) is the most common ectatic corneal disease, with clinical findings that include discomfort, visual disturbance and possible blindness if left untreated. KC affects approximately 1:400 to 1:2000 people worldwide, including both males and females. The aetiology and onset of KC remains a puzzle and as a result, the ability to treat or reverse the disease is hampered. Sex hormones are known to play a role in the maintenance of the structure and integrity of the human cornea. Hormone levels have been reported to alter corneal thickness, curvature, and sensitivity during different times of menstrual cycle. Surprisingly, the role of sex hormones in corneal diseases and KC has been largely neglected. Prolactin-induced protein, known to be regulated by sex hormones, is a new KC biomarker that has been recently proposed. Studies herein discuss the role of sex hormones as a control mechanism for KC onset and progression and evidence supporting the view that prolactin-induced protein is an important hormonally regulated biomarker in KC is discussed.
Keywords: Bodily fluids; Human cornea; Keratoconus; Prolactin-induced protein; Sex hormones.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






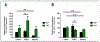
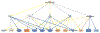


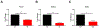
References
-
- Amsler M, 1946. Kératocône classique et kératocône fruste; arguments unitaires. Ophthalmologica 111, 96–101. - PubMed
-
- Annibalini G, Agostini D, Calcabrini C, Martinelli C, Colombo E, Guescini M, Tibollo P, Stocchi V, Sestili P, 2014. Effects of sex hormones on inflammatory response in male and female vascular endothelial cells. J. Endocrinol. Invest 37, 861–869. - PubMed
-
- Anwar M, Teichmann KD, 2002. Deep lamellar keratoplasty: surgical techniques for anterior lamellar keratoplasty with and without baring of Descemet’s membrane. Cornea 21, 374–383. - PubMed
-
- Atilano SR, Coskun P, Chwa M, Jordan N, Reddy V, Le K, Wallace DC, Kenney MC, 2005. Accumulation of mitochondrial DNA damage in keratoconus corneas. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci 46, 1256–1263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

