Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding protein stimulates CD14-dependent Toll-like receptor 4 internalization and LPS-induced TBK1-IKKϵ-IRF3 axis activation
- PMID: 29760187
- PMCID: PMC6028956
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.796631
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding protein stimulates CD14-dependent Toll-like receptor 4 internalization and LPS-induced TBK1-IKKϵ-IRF3 axis activation
Abstract
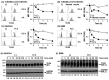
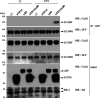
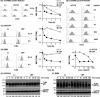
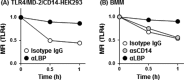
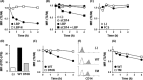
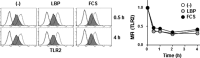
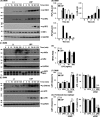
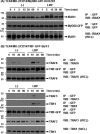
Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) is an indispensable immune receptor for lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a major component of the Gram-negative bacterial cell wall. Following LPS stimulation, TLR4 transmits the signal from the cell surface and becomes internalized in an endosome. However, the spatial regulation of TLR4 signaling is not fully understood. Here, we investigated the mechanisms of LPS-induced TLR4 internalization and clarified the roles of the extracellular LPS-binding molecules, LPS-binding protein (LBP), and glycerophosphatidylinositol-anchored protein (CD14). LPS stimulation of CD14-expressing cells induced TLR4 internalization in the presence of serum, and an inhibitory anti-LBP mAb blocked its internalization. Addition of LBP to serum-free cultures restored LPS-induced TLR4 internalization to comparable levels of serum. The secretory form of the CD14 (sCD14) induced internalization but required a much higher concentration than LBP. An inhibitory anti-sCD14 mAb was ineffective for serum-mediated internalization. LBP lacking the domain for LPS transfer to CD14 and a CD14 mutant with reduced LPS binding both attenuated TLR4 internalization. Accordingly, LBP is an essential serum molecule for TLR4 internalization, and its LPS transfer to membrane-anchored CD14 (mCD14) is a prerequisite. LBP induced the LPS-stimulated phosphorylation of TBK1, IKKϵ, and IRF3, leading to IFN-β expression. However, LPS-stimulated late activation of NF-κB or necroptosis were not affected. Collectively, our results indicate that LBP controls LPS-induced TLR4 internalization, which induces TLR adaptor molecule 1 (TRIF)-dependent activation of the TBK1-IKKϵ-IRF3-IFN-β pathway. In summary, we showed that LBP-mediated LPS transfer to mCD14 is required for serum-dependent TLR4 internalization and activation of the TRIF pathway.
Keywords: CD14; LPS-binding protein (LBP); TIR-domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-B (TRIF); Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4); cell-surface receptor; endotoxin; innate immunity; lipopolysaccharide (LPS); pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP); pattern recognition receptor (PRR).
© 2018 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein-mediated Toll-like receptor 4 dimerization enables rapid signal transduction against lipopolysaccharide stimulation on membrane-associated CD14-expressing cells.Int Immunol. 2010 Apr;22(4):271-80. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxq005. Epub 2010 Feb 4. Int Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20133493
-
Oxidized phospholipid inhibition of toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling is restricted to TLR2 and TLR4: roles for CD14, LPS-binding protein, and MD2 as targets for specificity of inhibition.J Biol Chem. 2008 Sep 5;283(36):24748-59. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M800352200. Epub 2008 Jun 17. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18559343 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic lipopolysaccharide transfer cascade to TLR4/MD2 complex via LBP and CD14.BMB Rep. 2017 Feb;50(2):55-57. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2017.50.2.011. BMB Rep. 2017. PMID: 28115037 Free PMC article.
-
Modulatory effects of sCD14 and LBP on LPS-host cell interactions.J Endotoxin Res. 2005;11(4):225-9. doi: 10.1179/096805105X46565. J Endotoxin Res. 2005. PMID: 16176659 Review.
-
TLR4 and CD14 trafficking and its influence on LPS-induced pro-inflammatory signaling.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Feb;78(4):1233-1261. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03656-y. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33057840 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Facilitation of Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract Microbiome-Derived Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Entry Into Human Neurons by Amyloid Beta-42 (Aβ42) Peptide.Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Dec 6;13:545. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00545. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31866832 Free PMC article.
-
The Probiotic Properties of Lactic Acid Bacteria and Their Applications in Animal Husbandry.Curr Microbiol. 2021 Dec 14;79(1):22. doi: 10.1007/s00284-021-02722-3. Curr Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34905106 Review.
-
Ergosta-7, 9 (11), 22-trien-3β-ol Interferes with LPS Docking to LBP, CD14, and TLR4/MD-2 Co-Receptors to Attenuate the NF-κB Inflammatory Pathway In Vitro and Drosophila.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 17;22(12):6511. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126511. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34204506 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNA PAPPA-AS1 Induces the Development of Hypertrophic Scar by Upregulating TLR4 through Interacting with TAF15.Mediators Inflamm. 2021 Jul 3;2021:3170261. doi: 10.1155/2021/3170261. eCollection 2021. Mediators Inflamm. 2021. PMID: 34285657 Free PMC article.
-
TRIF-dependent signaling and its role in liver diseases.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Apr 17;12:1370042. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1370042. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38694821 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

