Aurora A-dependent CENP-A phosphorylation at inner centromeres protects bioriented chromosomes against cohesion fatigue
- PMID: 29760389
- PMCID: PMC5951908
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-04089-9
Aurora A-dependent CENP-A phosphorylation at inner centromeres protects bioriented chromosomes against cohesion fatigue
Abstract
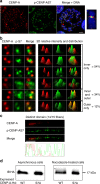
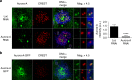
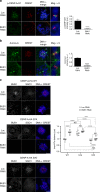
Sustained spindle tension applied to sister centromeres during mitosis eventually leads to uncoordinated loss of sister chromatid cohesion, a phenomenon known as "cohesion fatigue." We report that Aurora A-dependent phosphorylation of serine 7 of the centromere histone variant CENP-A (p-CENP-AS7) protects bioriented chromosomes against cohesion fatigue. Expression of a non-phosphorylatable version of CENP-A (CENP-AS7A) weakens sister chromatid cohesion only when sister centromeres are under tension, providing the first evidence of a regulated mechanism involved in protection against passive cohesion loss. Consistent with this observation, p-CENP-AS7 is detected at the inner centromere where it forms a discrete domain. The depletion or inhibition of Aurora A phenocopies the expression of CENP-AS7A and we show that Aurora A is recruited to centromeres in a Bub1-dependent manner. We propose that Aurora A-dependent phosphorylation of CENP-A at the inner centromere protects chromosomes against tension-induced cohesion fatigue until the last kinetochore is attached to spindle microtubules.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

