Silicon-chip-based mid-infrared dual-comb spectroscopy
- PMID: 29760418
- PMCID: PMC5951801
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-04350-1
Silicon-chip-based mid-infrared dual-comb spectroscopy
Abstract
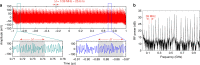
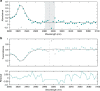
The development of a spectroscopy device on a chip that could realize real-time fingerprinting with label-free and high-throughput detection of trace molecules represents one of the big challenges in sensing. Dual-comb spectroscopy (DCS) in the mid-infrared is a powerful technique offering high acquisition rates and signal-to-noise ratios through use of only a single detector with no moving parts. Here, we present a nanophotonic silicon-on-insulator platform designed for mid-infrared (mid-IR) DCS. A single continuous-wave low-power pump source generates two mutually coherent mode-locked frequency combs spanning from 2.6 to 4.1 μm in two silicon microresonators. A proof-of-principle experiment of vibrational absorption DCS in the liquid phase is achieved acquiring spectra of acetone spanning from 2900 to 3100 nm at 127-GHz (4.2-cm-1) resolution. These results represent a significant step towards a broadband, mid-IR spectroscopy instrument on a chip for liquid/condensed matter phase studies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
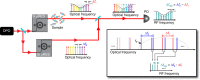
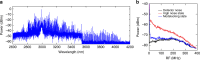
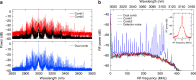
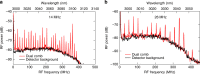
References
-
- Bernhardt B, et al. Mid-infrared dual-comb spectroscopy with 2.4 μm Cr2+:ZnSe femtosecond lasers. Appl. Phys. B. 2010;100:3–8. doi: 10.1007/s00340-010-4080-0. - DOI
-
- Bernhardt B, et al. Cavity-enhanced dual-comb spectroscopy. Nat. Photon. 2010;4:55–57. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2009.217. - DOI
-
- Baumann E, et al. Spectroscopy of the methane ν3 band with an accurate midinfrared coherent dual-comb spectrometer. Phys. Rev. A. 2011;84:062513. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.84.062513. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

