The gut microbiota and the brain-gut-kidney axis in hypertension and chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 29760448
- PMCID: PMC6385605
- DOI: 10.1038/s41581-018-0018-2
The gut microbiota and the brain-gut-kidney axis in hypertension and chronic kidney disease
Abstract
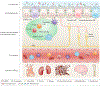
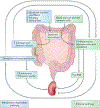
Crosstalk between the gut microbiota and the host has attracted considerable attention owing to its involvement in diverse diseases. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is commonly associated with hypertension and is characterized by immune dysregulation, metabolic disorder and sympathetic activation, which are all linked to gut dysbiosis and altered host-microbiota crosstalk. In this Review, we discuss the complex interplay between the brain, the gut, the microbiota and the kidney in CKD and hypertension and explain our brain-gut-kidney axis hypothesis for the pathogenesis of these diseases. Consideration of the role of the brain-gut-kidney axis in the maintenance of normal homeostasis and of dysregulation of this axis in CKD and hypertension could lead to the identification of novel therapeutic targets. In addition, the discovery of unique microbial communities and their associated metabolites and the elucidation of brain-gut-kidney signalling are likely to fill fundamental knowledge gaps leading to innovative research, clinical trials and treatments for CKD and hypertension.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Jha V et al. Chronic kidney disease: global dimension and perspectives. Lancet 382, 260–272 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Rao MV, Qiu Y, Wang C & Bakris G Hypertension and CKD: Kidney Early Evaluation Program (KEEP) and National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), 1999–2004. Am. J. Kidney Dis 51, S30–S37 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Inker LA et al. KDOQI US commentary on the 2012 KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 63, 713–735 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Andrassy KM Comments on ‘KDIGO 2012 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease’. Kidney Int. 84, 622–623 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

