5-ALA fluorescence and laser Doppler flowmetry for guidance in a stereotactic brain tumor biopsy
- PMID: 29760987
- PMCID: PMC5946788
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.9.002284
5-ALA fluorescence and laser Doppler flowmetry for guidance in a stereotactic brain tumor biopsy
Abstract
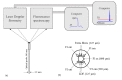
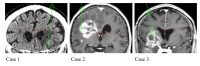
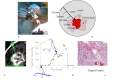
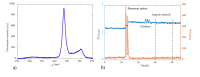
A fiber optic probe was developed for guidance during stereotactic brain biopsy procedures to target tumor tissue and reduce the risk of hemorrhage. The probe was connected to a setup for the measurement of 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA) induced fluorescence and microvascular blood flow. Along three stereotactic trajectories, fluorescence (n = 109) and laser Doppler flowmetry (LDF) (n = 144) measurements were done in millimeter increments. The recorded signals were compared to histopathology and radiology images. The median ratio of protoporphyrin IX (PpIX) fluorescence and autofluorescence (AF) in the tumor was considerably higher than the marginal zone (17.3 vs 0.9). The blood flow showed two high spots (3%) in total. The proposed setup allows simultaneous and real-time detection of tumor tissue and microvascular blood flow for tracking the vessels.
Keywords: (000.0000) General; (000.2700) General science.
Conflict of interest statement
NH, JCOR, KW: (P).
Figures

References
-
- Owen C. M., Linskey M. E., “Frame-based stereotaxy in a frameless era: current capabilities, relative role, and the positive- and negative predictive values of blood through the needle,” J. Neurooncol. 93(1), 139–149 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Kim J. E., Kim D. G., Paek S. H., Jung H.-W., “Stereotactic biopsy for intracranial lesions: reliability and its impact on the planning of treatment,” Acta Neurochir. (Wien) 145(7), 547–554, discussion 554–555 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Ivan M. E., Yarlagadda J., Saxena A. P., Martin A. J., Starr P. A., Sootsman W. K., Larson P. S., “Brain shift during bur hole-based procedures using interventional MRI,” J. Neurosurg. 121(1), 149–160 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Chen C.-C., Hsu P.-W., Erich Wu T.-W., Lee S.-T., Chang C.-N., Wei K. C., Chuang C. C., Wu C. T., Lui T. N., Hsu Y. H., Lin T. K., Lee S. C., Huang Y. C., “Stereotactic brain biopsy: Single center retrospective analysis of complications,” Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 111(10), 835–839 (2009). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
