Using ZFIN: Data Types, Organization, and Retrieval
- PMID: 29761463
- PMCID: PMC6319390
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7737-6_11
Using ZFIN: Data Types, Organization, and Retrieval
Abstract
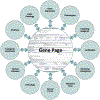
The Zebrafish Model Organism Database (ZFIN; zfin.org) was established in 1994 as the primary genetic and genomic resource for the zebrafish research community. Some of the earliest records in ZFIN were for people and laboratories. Since that time, services and data types provided by ZFIN have grown considerably. Today, ZFIN provides the official nomenclature for zebrafish genes, mutants, and transgenics and curates many data types including gene expression, phenotypes, Gene Ontology, models of human disease, orthology, knockdown reagents, transgenic constructs, and antibodies. Ontologies are used throughout ZFIN to structure these expertly curated data. An integrated genome browser provides genomic context for genes, transgenics, mutants, and knockdown reagents. ZFIN also supports a community wiki where the research community can post new antibody records and research protocols. Data in ZFIN are accessible via web pages, download files, and the ZebrafishMine (zebrafishmine.org), an installation of the InterMine data warehousing software. Searching for data at ZFIN utilizes both parameterized search forms and a single box search for searching or browsing data quickly. This chapter aims to describe the primary ZFIN data and services, and provide insight into how to use and interpret ZFIN searches, data, and web pages.
Keywords: Danio rerio; Database; Genetics; Genomics; ZFIN; Zebrafish Information Network.
Figures












References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

