Role of SdiA on Biofilm Formation by Atypical Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli
- PMID: 29762495
- PMCID: PMC5977193
- DOI: 10.3390/genes9050253
Role of SdiA on Biofilm Formation by Atypical Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli
Abstract
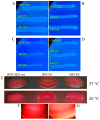
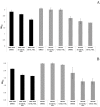
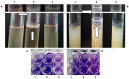
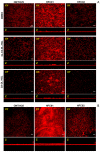
Atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli are capable to form biofilm on biotic and abiotic surfaces, regardless of the adherence pattern displayed. Several E. coli mechanisms are regulated by Quorum sensing (QS), including virulence factors and biofilm formation. Quorum sensing is a signaling system that confers bacteria with the ability to respond to chemical molecules known as autoinducers. Suppressor of division inhibitor (SdiA) is a QS receptor present in atypical enteropathogenic E.coli (aEPEC) that detects acyl homoserine lactone (AHL) type autoinducers. However, these bacteria do not encode an AHL synthase, but they are capable of sensing AHL molecules produced by other species, establishing an inter-species bacterial communication. In this study, we performed experiments to evaluate pellicle, ring-like structure and biofilm formation on wild type, sdiA mutants and complemented strains. We also evaluated the transcription of genes involved in different stages of biofilm formation, such as bcsA, csgA, csgD, fliC and fimA. The sdiA mutants were capable of forming thicker biofilm structures and showed increased motility when compared to wild type and complemented strains. Moreover, they also showed denser pellicles and ring-like structures. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis demonstrated increased csgA, csgD and fliC transcription on mutant strains. Biofilm formation, as well as csgD, csgA and fimA transcription decreased on wild type strains by the addition of AHL. These results indicate that SdiA participates on the regulation of these phenotypes in aEPEC and that AHL addition enhances the repressor effect of this receptor on the transcription of biofilm and motility related genes.
Keywords: acyl homoserine lactone; atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli; biofilm formation; confocal scanning laser microscopy; sdiA gene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kaper J.B. Defining enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Rev. Microbiol. 1996;27:130–133.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

