Synergistic Inhibition of Thalidomide and Icotinib on Human Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinomas Through ERK and AKT Signaling
- PMID: 29763936
- PMCID: PMC5978026
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.909977
Synergistic Inhibition of Thalidomide and Icotinib on Human Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinomas Through ERK and AKT Signaling
Abstract
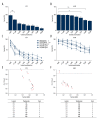
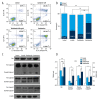
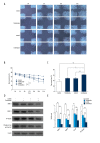
BACKGROUND Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) have been widely used in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with sensitive EGFR mutations. However, the survival of patients with EGFR-TKI administration is limited by the inevitable development of acquired drug resistance. Recently, multi-targeted drugs combination has been shown to be a promising strategy to improve the efficacy of EGFR-TKI treatment and enable the reduction of drug resistance in NSCLC. MATERIAL AND METHODS Humanized NSCLC cell lines PC9 and A549 were co-cultured with thalidomide and/or icotinib to test for anti-tumor efficiency. Cell proliferation was measured by MTT assay, cell apoptosis by flow cytometry and cell migration by wound healing assay. Western blot was performed to determine the expression of caspase-3, -8, -9, Bax, EGFR, VEGF-R, AKT, ERK, MMP2, MMP9, and NF-κB. The xenograft mouse model was used to explore the effects of thalidomide and icotinib in vivo. Immunohistochemical testing was used to determine the expression of Ki-67 and TUNEL staining in tumor tissues. RESULTS Treatments of thalidomide and/or icotinib reduced cell viability, induced apoptosis, and suppressed migration. Attenuation of pEGFR and pVEGF-R resulted in deactivation of ERK and AKT pathways, which eventually increased the anti-proliferative response. In PC9 xenograft model, combined administration of thalidomide and icotinib restrained tumor growth with remarkable reduced Ki-67 index and increased TUNEL positive cells. CONCLUSIONS Thalidomide sensitizes icotinib to increase apoptosis and prevent migration, and it may be a potentially promising anti-tumor drug in lung cancer multi-modality therapy.
Figures


References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Walker S. Updates in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2008;12(4):587–96. - PubMed
-
- Hirsch FR, Varellagarcia M, Cappuzzo F. Predictive value of EGFR and HER2 overexpression in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncogene. 2009;28(1):32–37. - PubMed
-
- Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(25):2380–88. - PubMed
-
- Tsao MS, Sakurada A, Cutz JC, et al. Erlotinib in lung cancer – molecular and clinical predictors of outcome. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(353):133–44. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

