Immunological changes with kinase inhibitor therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- PMID: 29764250
- PMCID: PMC6237652
- DOI: 10.1080/10428194.2018.1457147
Immunological changes with kinase inhibitor therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Abstract
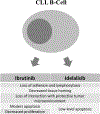
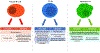
Ibrutinib and idelalisib are kinase inhibitors that have revolutionized the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Capable of inducing durable remissions, these agents also modulate the immune system. Both ibrutinib and idelalisib abrogate the tumor-supporting microenvironment by disrupting cell-cell interactions, modulating the T-cell compartment, and altering the cytokine milieu. Ibrutinib also partially restores T-cell and myeloid defects associated with CLL. In contrast, immune-related adverse effects, including pneumonitis, colitis, hepatotoxicity, and infections are of particular concern with idelalisib. While opportunistic infections and viral reactivations occur with both ibrutinib and idelalisib, these complications are less common and less severe with ibrutinib, especially when used as monotherapy without additional immunosuppressive agents. This review discusses the impact of ibrutinib and idelalisib on the immune system, including infectious and auto-immune complications as well as their specific effects on the B-cell, T-cell, and myeloid compartment.
Keywords: Lymphoid leukemia; T-cell mediated immunity; signaling therapies; the humoral immune response.
Figures
References
-
- Hallek M, Fischer K, Fingerle-Rowson G, et al. Addition of rituximab to fludarabine and cyclophosphamide in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2010. October 2;376(9747):1164–74. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61381-5. PubMed PMID: . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Eichhorst B, Fink AM, Bahlo J, et al. First-line chemoimmunotherapy with bendamustine and rituximab versus fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab in patients with advanced chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL10): an international, open-label, randomised, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016. July;17(7):928–42. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(16)30051-1. PubMed PMID: . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Badoux XC, Keating MJ, Wang X, et al. Fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab chemoimmunotherapy is highly effective treatment for relapsed patients with CLL. Blood. 2011. March 17;117(11):3016–24. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-08-304683. PubMed PMID: ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4123386. eng. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Robak T, Dmoszynska A, Solal-Celigny P, et al. Rituximab plus fludarabine and cyclophosphamide prolongs progression-free survival compared with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide alone in previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2010. April 01;28(10):1756–65. doi: 10.1200/jco.2009.26.4556. PubMed PMID: ; eng. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources