Talimogene Laherparepvec combined with anti-PD-1 based immunotherapy for unresectable stage III-IV melanoma: a case series
- PMID: 29764498
- PMCID: PMC5954455
- DOI: 10.1186/s40425-018-0337-7
Talimogene Laherparepvec combined with anti-PD-1 based immunotherapy for unresectable stage III-IV melanoma: a case series
Abstract
Background: Talimogene Laherparepvec (T-VEC) is an oncolytic virus approved as an intratumoral therapy for treating unresectable stage IIIB-IV metastatic melanoma. The mechanisms of action for T-VEC and checkpoint inhibitor are highly complementary. Recent studies have shown that combining checkpoint inhibitor therapy with T-VEC injection can lead to improved response rates for stage IIIB-IV melanoma patients.
Methods: We reviewed 10 consecutive cases of stage IIIC to stage IVM1b melanoma patients that received T-VEC plus checkpoint inhibitor(s) therapy (pembrolizumab, ipilimumab/nivolumab, or nivolumab) treated between June 2016 and August 2017 at the Cleveland Clinic with a median follow-up of 7 months (range: 4 to 13 months). Responses of injected (on-target) and uninjected (off-target) lesions were evaluated according to RECIST 2.0.
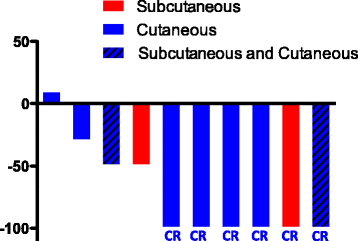
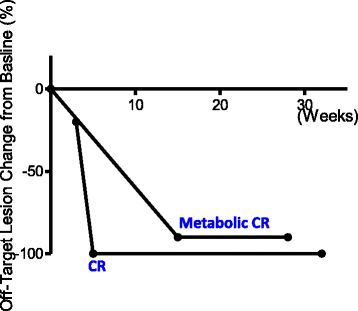
Results: The overall response rate for on-target lesions was 90%, with 6 patients experiencing a complete response in injected lesions. Two patients had off-target lesions, which were completely resolved after treatment. Blood samples were tested for 3 complete responders and 2 partial responders. CD4:CD8 ratio and frequencies of circulating PD1+ CD4 and CD8 T cells were elevated in complete responders but not partial responders. One patient died due to causes unrelated to melanoma and one patient died of progression of the disease.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that combining checkpoint inhibitor(s) with T-VEC injection may provide a synergistic efficacy for patients with unresectable melanoma. We observed a better overall response rate and complete response rate compared to published studies on similar therapeutic regimens.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ information
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Cleveland Clinic Institutional Review Boards.
Consent for publication
Informed consent has been obtained and are held by the authors.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures




References
-
- Poh A. First oncolytic viral therapy for melanoma. Cancer Discov. 2016;6(1):6. - PubMed
-
- Puzanov I, Milhem MM, Minor D, Hamid O, Li A, Chen L, Chastain M, Gorski KS, Anderson A, Chou J, et al. Talimogene Laherparepvec in combination with Ipilimumab in previously untreated, Unresectable stage IIIB-IV melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(22):2619–2626. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.67.1529. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andtbacka RH, Kaufman HL, Collichio F, Amatruda T, Senzer N, Chesney J, Delman KA, Spitler LE, Puzanov I, Agarwala SS, et al. Talimogene Laherparepvec improves durable response rate in patients with advanced melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(25):2780–2788. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.58.3377. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Harrington KJ, Andtbacka RH, Collichio F, Downey G, Chen L, Szabo Z, Kaufman HL. Efficacy and safety of talimogene laherparepvec versus granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in patients with stage IIIB/C and IVM1a melanoma: subanalysis of the phase III OPTiM trial. Onco Targets Ther. 2016;9:7081–7093. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S115245. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andtbacka RH, Ross M, Puzanov I, Milhem M, Collichio F, Delman KA, Amatruda T, Zager JS, Cranmer L, Hsueh E, et al. Patterns of clinical response with Talimogene Laherparepvec (T-VEC) in patients with melanoma treated in the OPTiM phase III clinical trial. Ann Surg Oncol. 2016;23(13):4169–4177. doi: 10.1245/s10434-016-5286-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
