EYA4 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth and invasion by suppressing NF-κB-dependent RAP1 transactivation
- PMID: 29764501
- PMCID: PMC5993152
- DOI: 10.1186/s40880-018-0276-1
EYA4 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth and invasion by suppressing NF-κB-dependent RAP1 transactivation
Abstract
Background: Our previous studies demonstrated that eyes absent homolog 4 (EYA4), a member of the eye development-related EYA family in Drosophila, is frequently methylated and silenced in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) specimens and associated with shorter survival. The current work aimed to explore the mechanisms through which EYA4 functions as a tumor suppressor in HCC.
Methods: Stable EYA4-expressing plasmid (pEYA4) transfectants of the human HCC cell lines Huh-7 and PLC/PRF/5 (PLC) were established. Xenografts tumors were established via subcutaneous injection of the stable transfectants into BALB/c nude mice. Tissue samples were obtained from 75 pathologically diagnosed HCC patients. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, Western blotting and immunohistochemistry were performed to determine the expression of EYA4 in cell lines, xenografts and clinical specimens. The cell proliferation, colony formation, invasiveness and tumor formation of stable transfectants were studied. A gene expression microarray was utilized to screen genes regulated by EYA4 expression. The effect of EYA4 on nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB)/RAS-related protein 1 (RAP1) signaling was demonstrated through the co-transfection of pEYA4 and Flag-tagged RAS-related protein 1A gene-expressing plasmid (Flag-RAP1A), functional studies, chromatin immunoprecipitation, immunofluorescence staining and cellular ubiquitination assay.
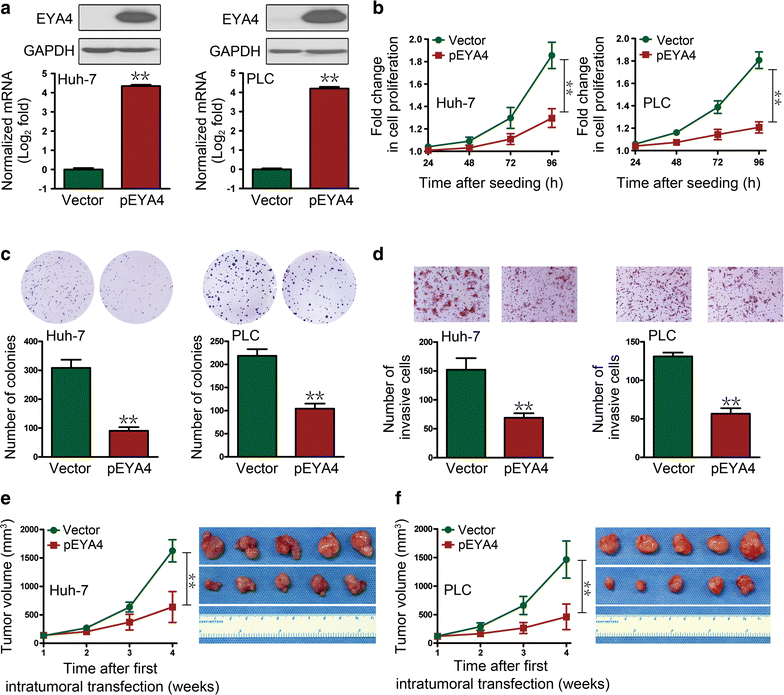
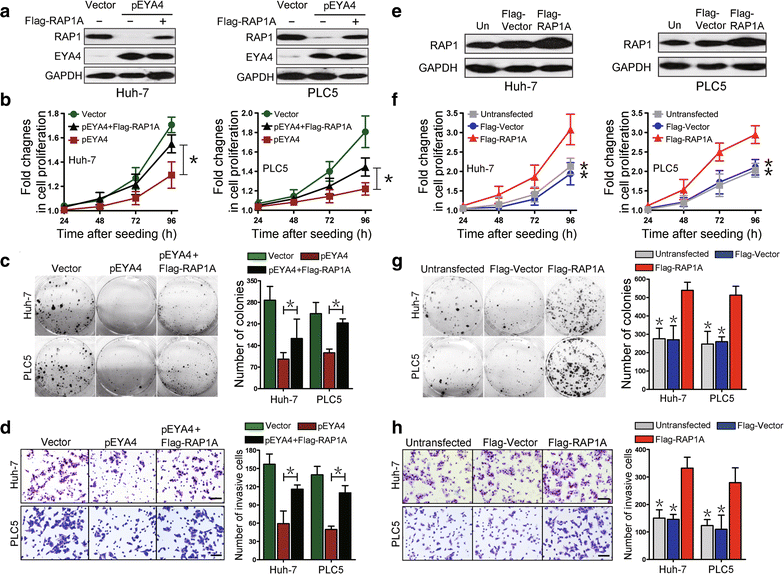
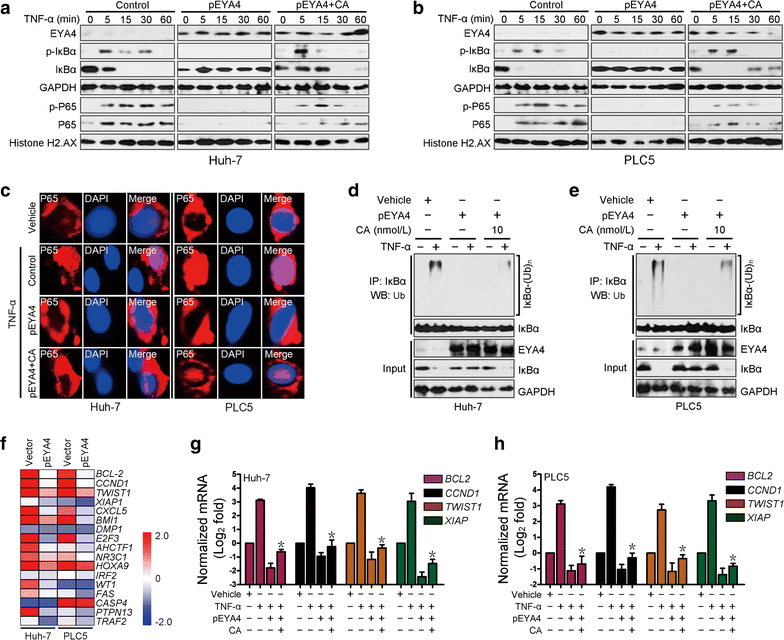
Results: The restoration of EYA4 expression in HCC cell lines suppressed cell proliferation, inhibited clonogenic outgrowth, reduced cell invasion and restrained xenograft tumor growth, and Flag-RAP1A reversed the suppressive effects of pEYA4 in vitro. Activation of NF-κB with tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) increased the binding of p65 to the RAP1A gene promoter and up-regulated RAP1 protein expression. The inhibition of NF-κB with BAY 11-7085 and p65 siRNA successfully blocked TNF-α-induced RAP1 up-regulation. EYA4 antagonized the TNF-α-induced phosphorylation and ubiquitination of inhibitor of NF-κBα (IκBα) as well as the nuclear translocation and transactivation of p65, resulting in repressed NF-κB activity and RAP1 expression. Blocking the serine/threonine phosphatase activity of EYA4 with calyculin A notably abrogated its suppressive effect on NF-κB activity. In addition, EYA4 expression was inversely correlated with IκBα/RAP1 activity in clinical HCC specimens.
Conclusion: Our findings provide a functional and mechanistic basis for identifying EYA4 as a bona fide tumor suppressor that disrupts aberrant activation of the NF-κB/RAP1 signaling pathway and thus orchestrates a physiological impediment to HCC growth and invasion.
Keywords: Eyes absent homolog 4 (EYA4); Hepatocellular carcinoma; Nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB); RAS-related protein 1 (RAP1); Transactivation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Tumor necrosis factor α-induced protein 1 as a novel tumor suppressor through selective downregulation of CSNK2B blocks nuclear factor-κB activation in hepatocellular carcinoma.EBioMedicine. 2020 Jan;51:102603. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.102603. Epub 2020 Jan 3. EBioMedicine. 2020. PMID: 31901862 Free PMC article.
-
Yin Yang 1-mediated epigenetic silencing of tumour-suppressive microRNAs activates nuclear factor-κB in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Pathol. 2016 Apr;238(5):651-64. doi: 10.1002/path.4688. J Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26800240
-
EYA4 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma by repressing MYCBP by dephosphorylating β-catenin at Ser552.Cancer Sci. 2019 Oct;110(10):3110-3121. doi: 10.1111/cas.14159. Epub 2019 Aug 28. Cancer Sci. 2019. PMID: 31385398 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted role of NF-κB in hepatocellular carcinoma therapy: Molecular landscape, therapeutic compounds and nanomaterial approaches.Environ Res. 2023 Jul 1;228:115767. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.115767. Epub 2023 Mar 24. Environ Res. 2023. PMID: 36966991 Review.
-
Delineating the tumour-regulatory roles of EYA4.Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 Apr;210:115466. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115466. Epub 2023 Feb 25. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36849065 Review.
Cited by
-
Artemisia carvifolia Buch silver nanoparticles downregulate the Rap2A gene in liver cancer.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 6;13(1):21553. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-48946-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38057542 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA ACVR2A suppresses bladder cancer cells proliferation and metastasis through miR-626/EYA4 axis.Mol Cancer. 2019 May 17;18(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1025-z. Mol Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31101108 Free PMC article.
-
A novel DNA methylation-based model that effectively predicts prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma.Biosci Rep. 2021 Mar 26;41(3):BSR20203945. doi: 10.1042/BSR20203945. Biosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33634306 Free PMC article.
-
Role of long noncoding RNA-mediated competing endogenous RNA regulatory network in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Aug 7;26(29):4240-4260. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i29.4240. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32848331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EYA4 serves as a prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma and suppresses tumour angiogenesis and metastasis.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Jun;23(6):4208-4216. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14309. Epub 2019 Apr 7. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30957411 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, et al. GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 11. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer. 2013.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81472261/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 2014A030310033/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province/International
- 2015A030313032/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province/International
- 2013B021800122/Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province/International
- 201604020044/Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangzhou City/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

