Comparative genomic analysis of multidrug-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates
- PMID: 29765237
- PMCID: PMC5939923
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S147858
Comparative genomic analysis of multidrug-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates
Abstract
Introduction: Multidrug resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae has emerged as a serious problem to public health. A further understanding of the genetic diversity in antibiotic-resistant S. pneumoniae isolates is needed.
Methods: We conducted whole-genome resequencing for 25 pneumococcal strains isolated from children with different antimicrobial resistance profiles. Comparative analysis focus on detection of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and insertions and deletions (indels) was conducted. Moreover, phylogenetic analysis was applied to investigate the genetic relationship among these strains.
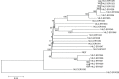
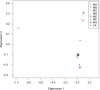
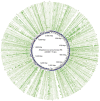
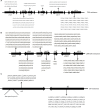
Results: The genome size of the isolates was ~2.1 Mbp, covering >90% of the total estimated size of the reference genome. The overall G+C% content was ~39.5%, and there were 2,200-2,400 open reading frames. All isolates with different drug resistance profiles harbored many indels (range 131-171) and SNPs (range 16,103-28,128). Genetic diversity analysis showed that the variation of different genes were associated with specific antibiotic resistance. Known antibiotic resistance genes (pbps, murMN, ciaH, rplD, sulA, and dpr) were identified, and new genes (regR, argH, trkH, and PTS-EII) closely related with antibiotic resistance were found, although these genes were primarily annotated with functions in virulence as well as carbohydrate and amino acid transport and metabolism. Phylogenetic analysis unambiguously indicated that isolates with different antibiotic resistance profiles harbored similar genetic backgrounds. One isolate, 14-LC.ER1025, showed a much weaker phylogenetic relationship with the other isolates, possibly caused by genomic variation.
Conclusion: In this study, although pneumococcal isolates had similar genetic backgrounds, strains were diverse at the genomic level. These strains exhibited distinct variations in their indel and SNP compositions associated with drug resistance.
Keywords: SNPs; Streptococcus pneumoniae; antimicrobial resistance; insertions/deletions; phylogenetic analysis; whole-genome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure All authors report no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative genomic analysis of ten clinical Streptococcus pneumoniae collected from a Malaysian hospital reveal 31 new unique drug-resistant SNPs using whole genome sequencing.J Biomed Sci. 2018 Feb 15;25(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s12929-018-0414-8. J Biomed Sci. 2018. PMID: 29448938 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomic analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolates.BMC Genomics. 2014 Jun 13;15(1):469. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-469. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24923884 Free PMC article.
-
Population genetic structure, serotype distribution and antibiotic resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae causing invasive disease in children in Argentina.Microb Genom. 2021 Sep;7(9):000636. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000636. Microb Genom. 2021. PMID: 34586054 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomic analysis and multi-drug resistance differences of Acinetobacter baumannii in Chongqing, China.Infect Drug Resist. 2019 Sep 11;12:2827-2838. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S216745. eCollection 2019. Infect Drug Resist. 2019. PMID: 31571939 Free PMC article.
-
CIRCULATING CLONAL COMPLEXES AND SEQUENCE TYPES OF STREPTOCOCCUS PNEUMONIAE SEROTYPE 19A WORLDWIDE: THE IMPORTANCE OF MULTIDRUG RESISTANCE: A SYSTEMATIC LITERATURE REVIEW.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2021 Jan;20(1):45-57. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2021.1873136. Epub 2021 Feb 17. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2021. PMID: 33507135
Cited by
-
Whole genomic comparative analysis of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 1 isolates causing invasive and non-invasive infections among children under 5 years in Casablanca, Morocco.BMC Genomics. 2021 Jan 7;22(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-07316-0. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33413118 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorometric Liposome Screen for Inhibitors of a Physiologically Important Bacterial Ion Channel.Front Microbiol. 2021 Mar 1;12:603700. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.603700. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33732218 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-Genome Analysis-Based Phylogeographic Investigation of Streptococcus pneumoniae Serotype 19A Sequence Type 320 Isolates in Japan.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022 Feb 15;66(2):e0139521. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01395-21. Epub 2021 Dec 20. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022. PMID: 34930035 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Genome Analysis of Streptococcus suis Serotype 9 Isolates from China, The Netherland, and the U.K.Life (Basel). 2021 Nov 30;11(12):1324. doi: 10.3390/life11121324. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34947855 Free PMC article.
-
Ciprofloxacin induced antibiotic resistance in Salmonella Typhimurium mutants and genome analysis.Arch Microbiol. 2021 Dec;203(10):6131-6142. doi: 10.1007/s00203-021-02577-z. Epub 2021 Sep 28. Arch Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34585273
References
-
- World Health Organization Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine for childhood immunization: WHO position paper. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2007;82(12):93–104. - PubMed
-
- Kim SH, Song JH, Chung DR, et al. ANSORP Study Group Changing trends in antimicrobial resistance and serotypes of Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates in Asian countries: an Asian Network for Surveillance of Resistant Pathogens (ANSORP) study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012;56(3):1418–1426. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cherazard R, Epstein M, Doan TL, Salim T, Bharti S, Smith MA. Antimicrobial resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae: prevalence, mechanisms, and clinical implications. Am J Ther. 2017;24(3):e361–e369. - PubMed
-
- Schweizer I, Blättner S, Maurer P, et al. New aspects of the interplay between penicillin binding proteins, murM, and the two-component system CiaRH of penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae Serotype 19A isolates from Hungary. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;61(7):e00414–e00417. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

