Use of histamine H2 receptor antagonists and outcomes in patients with heart failure: a nationwide population-based cohort study
- PMID: 29765253
- PMCID: PMC5944448
- DOI: 10.2147/CLEP.S162909
Use of histamine H2 receptor antagonists and outcomes in patients with heart failure: a nationwide population-based cohort study
Abstract
Background: Histamine H2 receptor activation promotes cardiac fibrosis and apoptosis in mice. However, the potential effectiveness of histamine H2 receptor antagonists (H2RAs) in humans with heart failure is largely unknown. We examined the association between H2RA initiation and all-cause mortality among patients with heart failure.
Methods: Using Danish medical registries, we conducted a nationwide population-based active-comparator cohort study of new users of H2RAs and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) after first-time hospitalization for heart failure during the period 1995-2014. Hazard ratios (HRs) for all-cause mortality and hospitalization due to worsening of heart failure, adjusting for age, sex, and time between heart failure diagnosis and initiation of PPI or H2RA therapy, index year, comorbidity, cardiac surgery, comedications, and socioeconomic status were computed based on Cox regression analysis.
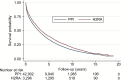
Results: Our analysis included 42,902 PPI initiators (median age 78 years, 46% female) and 3,296 H2RA initiators (median age 76 years, 48% female). Mortality risk was lower among H2RA initiators than PPI initiators after 1 year (26% vs 31%) and 5 years (60% vs 66%). In multivariable analyses, the 1-year HR was 0.80 (95% CI, 0.74-0.86) and the 5-year HR was 0.85 (95% CI, 0.80-0.89). These findings were consistent after propensity score matching and for ischemic and nonischemic heart failure, as for sex and age groups. The rate of hospitalization due to worsening of heart failure was lower among H2RA initiators than PPI initiators.
Conclusion: In patients with heart failure, H2RA initiation was associated with 15%-20% lower mortality than PPI initiation.
Keywords: epidemiology; heart failure; histamine H2 receptor; mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work
Figures

References
-
- Zeng Z, Shen L, Li X, et al. Disruption of histamine H2 receptor slows heart failure progression through reducing myocardial apoptosis and fibrosis. Clin Sci (Lond) 2014;127(7):435–448. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

