Evodiamine, a Novel NOTCH3 Methylation Stimulator, Significantly Suppresses Lung Carcinogenesis in Vitro and in Vivo
- PMID: 29765324
- PMCID: PMC5938359
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00434
Evodiamine, a Novel NOTCH3 Methylation Stimulator, Significantly Suppresses Lung Carcinogenesis in Vitro and in Vivo
Abstract
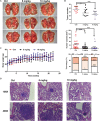
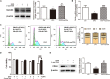
Lung cancer is a leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. NOTCH3 signaling is mainly expressed in non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC), and has been proposed as a therapeutic target of NSCLC. While, few agents for preventing or treating NSCLC via targeting NOTCH3 signaling are used in modern clinical practice. Evodiamine (EVO), an alkaloid derived from Euodiae Fructus, possesses low toxicity and has long been shown to exert anti-lung cancer activity. However, the underlying anti-lung cancer mechanisms of EVO are not yet fully understood. In this study, we explored the involvement of NOTCH3 signaling in the anti-lung cancer effects of EVO. Urethane-induced lung cancer mouse model and two NSCLC cell models, A549 and H1299, were used to evaluate the in vivo and in vitro anti-lung cancer action of EVO. A DNA methyltransferase inhibitor was employed to investigate the role of NOTCH3 signaling in the anti-lung cancer effects of EVO. Results showed that EVO potently reduced tumor size and tumor numbers in mice, and inhibited NOTCH3 in the tumors. EVO also dramatically reduced cell viability, induced G2/M cell cycle arrest, inhibited cell migration and reduced stemness in cultured NSCLC cells. Mechanistic studies showed that EVO potently inhibited NOTCH3 signaling by activation of DNMTs-induced NOTCH3 methylation. Importantly, inhibition of NOTCH3 methylation in NSCLC cells diminished EVO's anti-NSCLC effects. Collectively, EVO, a novel NOTCH3 methylation stimulator, exerted potent anti-lung cancer effects partially by inhibiting NOTCH3 signaling. These findings provide new insight into the EVO's anti-NSCLC action, and suggest a potential role of EVO in lung cancer prevention and treatment.
Keywords: DNA methyltransferases; NOTCH3 methylation; Notch3; evodiamine; lung cancer.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Evodiamine suppresses Notch3 signaling in lung tumorigenesis via direct binding to γ-secretases.Phytomedicine. 2020 Mar;68:153176. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153176. Epub 2020 Jan 31. Phytomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32045841
-
Evodiamine inhibits stemness and metastasis by altering the SOX9-β-catenin axis in non-small-cell lung cancer.J Cell Biochem. 2022 Sep;123(9):1454-1466. doi: 10.1002/jcb.30304. Epub 2022 Jul 5. J Cell Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35788981
-
Evodiamine suppresses the progression of non-small cell lung carcinoma via endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis pathway in vivo and in vitro.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2022 Jan-Dec;36:3946320221086079. doi: 10.1177/03946320221086079. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35388733 Free PMC article.
-
Progress on the effects and underlying mechanisms of evodiamine in digestive system diseases, and its toxicity: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Phytomedicine. 2024 Sep;132:155851. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155851. Epub 2024 Jul 6. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39018943
-
Evodiamine and Its Role in Chronic Diseases.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;929:315-328. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-41342-6_14. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27771931 Review.
Cited by
-
Traditional Chinese medicine Euodiae Fructus: botany, traditional use, phytochemistry, pharmacology, toxicity and quality control.Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2023 Feb 15;13(1):6. doi: 10.1007/s13659-023-00369-0. Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2023. PMID: 36790599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress on evodiamine, a bioactive alkaloid of Evodiae fructus: Focus on its anti-cancer activity and bioavailability (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2021 Nov;22(5):1327. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10762. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34630681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging agents that target signaling pathways in cancer stem cells.J Hematol Oncol. 2020 May 26;13(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00901-6. J Hematol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32456660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evodiamine as an anticancer agent: a comprehensive review on its therapeutic application, pharmacokinetic, toxicity, and metabolism in various cancers.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023 Feb;39(1):1-31. doi: 10.1007/s10565-022-09772-8. Epub 2022 Sep 23. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 36138312 Review.
-
Cancer Stem Cells Connecting to Immunotherapy: Key Insights, Challenges, and Potential Treatment Opportunities.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jun 23;17(13):2100. doi: 10.3390/cancers17132100. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40647402 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

