IgG4-related kidney disease: the effects of a Rituximab-based immunosuppressive therapy
- PMID: 29765543
- PMCID: PMC5940417
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.25095
IgG4-related kidney disease: the effects of a Rituximab-based immunosuppressive therapy
Abstract
IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a recently recognized disorder, characterized by elevated serum IgG4 concentrations, dense tissue infiltration of IgG4-positive plasma cells and storiform fibrosis. Treatment is usually based on steroids, however, relapses and long-term adverse effects are frequent. We prospectively studied 5 consecutive patients with histologically-proven IgG4-RD and renal involvement, treated with an extended Rituximab protocol combined with steroids. Two doses of intravenous cyclophosphamide were added in 4 patients. Five patients with IgG-RD were investigated: three had tubulointerstitial nephritis (TIN), while two had retroperitoneal fibrosis (RPF). In the patients with TIN, renal biospy was repeated after 1 year. In the patients with TIN, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) at 12 months increased from 9 to 24 ml/min per 1.73 m2; IgG/IgG4 decreased from 3,236/665 to 706/51 mg/dl; C3/C4 increased from 49/6 to 99/27 mg/dl; CD20+ B-cells decreased from 8.7% to 0.5%; Regulatory T-cells decreased from 7.2% to 2.5%. These functional and immunologic changes persisted at 24 months and in two patients at 36 months. A repeat renal biopsy in the patients with TIN showed a dramatic decrease in interstitial plasma cell infiltrate with normalization of IgG4/IgG positive plasma cells. The patients with RPF showed a huge regression of retroperitoneal tissue. In this sample of patients with aggressive IgG4-RD and renal involvement, treatment aimed at depleting B cells and decreasing antibody and cytokine production was associated with a substantial, persistent increase in eGFR, and a definite improvement in immunologic, radiologic and histological parameters.
Keywords: IgG4-related disease; IgG4-related kidney disease; Rituximab; retroperitoneal fibrosis; tubulointerstitial nephritis.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST All the authors declare no conflicts of interest. The results presented in this paper have not been published previously in whole or part, except in abstract format.
Figures
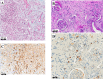

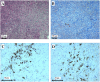
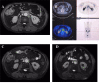

References
-
- Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:539–51. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1104650 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mahajan VS, Mattoo H, Deshpande V, Pillai SS, Stone JH. IgG4-related disease. Annu Rev Pathol. 2014;9:315–47. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathol-012513-104708 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kamisawa T, Zen Y, Pillai S, Stone JH. IgG4-related disease. Lancet. 2015;385:1460–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60720-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brito-Zerón P, Ramos-Casals M, Bosch X, Stone JH. The clinical spectrum of IgG4-related disease. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13:1203–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2014.08.013 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stone JH, Brito-Zerón P, Bosch X, Ramos-Casals M. Diagnostic Approach to the Complexity of IgG4-Related Disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 2015;90:927–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2015.03.020 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

