X-ray and cryo-EM structures of inhibitor-bound cytochrome bc1 complexes for structure-based drug discovery
- PMID: 29765610
- PMCID: PMC5947725
- DOI: 10.1107/S2052252518001616
X-ray and cryo-EM structures of inhibitor-bound cytochrome bc1 complexes for structure-based drug discovery
Abstract
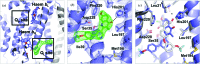
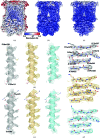
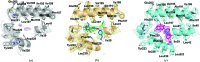
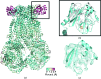
Cytochrome bc1, a dimeric multi-subunit electron-transport protein embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane, is a major drug target for the treatment and prevention of malaria and toxoplasmosis. Structural studies of cytochrome bc1 from mammalian homologues co-crystallized with lead compounds have underpinned structure-based drug design to develop compounds with higher potency and selectivity. However, owing to the limited amount of cytochrome bc1 that may be available from parasites, all efforts have been focused on homologous cytochrome bc1 complexes from mammalian species, which has resulted in the failure of some drug candidates owing to toxicity in the host. Crystallographic studies of the native parasite proteins are not feasible owing to limited availability of the proteins. Here, it is demonstrated that cytochrome bc1 is highly amenable to single-particle cryo-EM (which uses significantly less protein) by solving the apo and two inhibitor-bound structures to ∼4.1 Å resolution, revealing clear inhibitor density at the binding site. Therefore, cryo-EM is proposed as a viable alternative method for structure-based drug discovery using both host and parasite enzymes.
Keywords: cryo-EM; cryo-electron microscopy; cytochrome bc1; electron-transport chain; malaria; membrane proteins.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cryo-EM structure of the four-subunit Rhodobacter sphaeroides cytochrome bc1 complex in styrene maleic acid nanodiscs.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Mar 21;120(12):e2217922120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2217922120. Epub 2023 Mar 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 36913593 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Structure-Activity Analysis of Endochin-like Quinolones Reveals Potent Qi and Qo Site Inhibitors of Toxoplasma gondii and Plasmodium falciparum Cytochrome bc1 and Identifies ELQ-400 as a Remarkably Effective Compound against Acute Experimental Toxoplasmosis.ACS Infect Dis. 2018 Nov 9;4(11):1574-1584. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.8b00133. Epub 2018 Aug 30. ACS Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 30117728 Free PMC article.
-
Quinone binding sites of cyt bc complexes analysed by X-ray crystallography and cryogenic electron microscopy.Biochem Soc Trans. 2022 Apr 29;50(2):877-893. doi: 10.1042/BST20190963. Biochem Soc Trans. 2022. PMID: 35356963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design and use of photoactive ruthenium complexes to study electron transfer within cytochrome bc1 and from cytochrome bc1 to cytochrome c.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Nov-Dec;1827(11-12):1309-19. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2012.09.002. Epub 2012 Sep 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 22985600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure of the cytoplasmic ring of the Xenopus laevis nuclear pore complex.Science. 2022 Jun 10;376(6598):eabl8280. doi: 10.1126/science.abl8280. Epub 2022 Jun 10. Science. 2022. PMID: 35679404
Cited by
-
A splendid molecular factory: De- and reconstruction of the mammalian respiratory chain.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Mar 25;122(12):e2416162122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2416162122. Epub 2025 Mar 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40100632
-
Crystallography and the development of therapeutic medicines.IUCrJ. 2018 Feb 26;5(Pt 2):118-119. doi: 10.1107/S2052252518002555. eCollection 2018 Mar 1. IUCrJ. 2018. PMID: 29765598 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Ubiquinol-Reduction (Qi) Site of the Mitochondrial Cytochrome bc1 Complex for the Development of Next Generation Quinolone Antimalarials.Biology (Basel). 2022 Jul 25;11(8):1109. doi: 10.3390/biology11081109. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35892964 Free PMC article.
-
The expanding toolkit for structural biology: synchrotrons, X-ray lasers and cryoEM.IUCrJ. 2019 Mar 1;6(Pt 2):167-177. doi: 10.1107/S2052252519002422. eCollection 2019 Mar 1. IUCrJ. 2019. PMID: 30867914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dimeric structures of quinol-dependent nitric oxide reductases (qNORs) revealed by cryo-electron microscopy.Sci Adv. 2019 Aug 28;5(8):eaax1803. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aax1803. eCollection 2019 Aug. Sci Adv. 2019. PMID: 31489376 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams, P. D. et al. (2010). Acta Cryst. D66, 213–221.
-
- Anderson, A. C. (2003). Chem. Biol. 10, 787–797. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

