Two CuII complexes of 3,4,5-tri-methyl-1 H-pyrazole
- PMID: 29765723
- PMCID: PMC5947803
- DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018002359
Two CuII complexes of 3,4,5-tri-methyl-1 H-pyrazole
Abstract
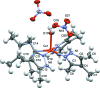
The crystal structure of complexes of 3,4,5-tri-methyl-1H-pyrazole with CuCl2·2H2O and Cu(NO3)2·2.5H2O are presented, namely di-μ-chlorido-bis[chloridobis(3,4,5-trimethyl-1H-pyrazole-κN2)copper(II)], [Cu2Cl4(C6H10N2)4] (1) and aquatetrakis(3,4,5-trimethyl-1H-pyrazole-κN2)copper(II) dinitrate, [Cu(C6H10N2)4(H2O)](NO3)2 (2), and compared to the previously determined structures for 3-methyl-1H-pyrazole and 3,5-di-methyl-1H-pyrazole. CuCl2 forms a 2:1 ligand-to-metal chloride-bridged complex with 3,4,5-tri-methyl-1H-pyrazole, with a square-pyramidal coordination geometry about each copper(II) center. Similarly to the previously obtained 3,5-di-methyl-1H-pyrazole complex with CuCl2, the pyrazole ligands are cis to each other, with two chloride ions bridging the two copper(II) centers, and a terminal chloride ion occupying the axial position. Cu(NO3)2 forms a 4:1 ligand-to-metal complex with 3,4,5-tri-methyl-1H-pyrazole that is also arranged in a square-pyramidal geometry about CuII. The newly obtained copper(II) complex has the same coordination geometry as the 3,5-di-methyl-1H-pyrazole complex, including an axial water mol-ecule, two nitrate ions hydrogen-bonded to the water mol-ecule, and four pyrazole ligands in the equatorial plane, suggesting that similar steric forces are at play in the formation of these complexes.
Keywords: chloride; complex; copper(II); crystal structure; metal organic; nitrate; trimethylpyrazole.
Figures
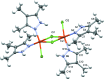
 − x, y, 1 − z. Hydrogen-atom labels are omitted for clarity.
− x, y, 1 − z. Hydrogen-atom labels are omitted for clarity.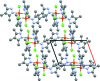
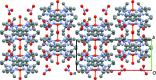
References
-
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–S19.
-
- Ardizzoia, G. A., Brenna, S., Durini, S., Therrien, B. & Trentin, I. (2013). Dalton Trans. 42, 12265–12273. - PubMed
-
- Barbour, L. J. (2001). J. Supramol. Chem. 1, 189–191.
-
- Bruker (2014). APEX2, SAINT, XPREP and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Denisova, T. O., Amelchenkova, E. V., Pruss, I. V., Dobrokhotova, Zh. V., Fialkovskii, O. P. & Nifedov, S. E. (2006). Zh. Neorg. Khim. 51, 1098–1142.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
