Designing of phenol-based β-carbonic anhydrase1 inhibitors through QSAR, molecular docking, and MD simulation approach
- PMID: 29765814
- PMCID: PMC5950840
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-018-1278-z
Designing of phenol-based β-carbonic anhydrase1 inhibitors through QSAR, molecular docking, and MD simulation approach
Abstract
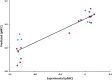
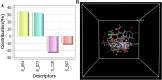
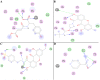
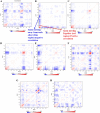
Tuberculosis (Tb) is an airborne infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Beta-carbonic anhydrase 1 (β-CA1) has emerged as one of the potential targets for new antitubercular drug development. In this work, three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationships (3D-QSAR), molecular docking, and molecular dynamics (MD) simulation approaches were performed on a series of natural and synthetic phenol-based β-CA1 inhibitors. The developed 3D-QSAR model (r2 = 0.94, q2 = 0.86, and pred_r2 = 0.74) indicated that the steric and electrostatic factors are important parameters to modulate the bioactivity of phenolic compounds. Based on this indication, we designed 72 new phenolic inhibitors, out of which two compounds (D25 and D50) effectively stabilized β-CA1 receptor and, thus, are potential candidates for new generation antitubercular drug discovery program.
Keywords: Docking; M. Tuberculosis; MD simulation; QSAR; β-Carbonic anhydrase 1.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standardsThere is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures






References
-
- Ahamad S, Rahman S, Khan FI, Dwivedi N, Ali S, Kim J, Imtaiyaz Hassan M. QSAR based therapeutic management of M. tuberculosis. Arch Pharm Res. 2017 - PubMed
-
- Ambriz-Pérez DL, Leyva-López N, Gutierrez-Grijalva EP, Heredia JB. Phenolic compounds: natural alternative in inflammation treatment. Rev Cogent Food Agric. 2016;2(1):1131412.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

