Beneficial Outcome of Urethane Treatment Following Status Epilepticus in a Rat Organophosphorus Toxicity Model
- PMID: 29766039
- PMCID: PMC5952304
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0070-18.2018
Beneficial Outcome of Urethane Treatment Following Status Epilepticus in a Rat Organophosphorus Toxicity Model
Abstract
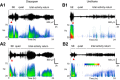
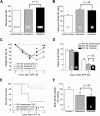
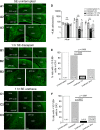
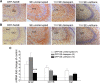
The efficacy of benzodiazepines to terminate electrographic status epilepticus (SE) declines the longer a patient is in SE. Therefore, alternative methods for ensuring complete block of SE and refractory SE are necessary. We compared the ability of diazepam and a subanesthetic dose of urethane to terminate prolonged SE and mitigate subsequent pathologies. Adult Sprague Dawley rats were injected with diisopropylfluorophosphate (DFP) to induce SE. Rats were administered diazepam (10 mg/kg, ip) or urethane (0.8 g/kg, s.c.) 1 h after DFP-induced SE and compared to rats that experienced uninterrupted SE. Large-amplitude and high-frequency spikes induced by DFP administration were quenched for at least 46 h in rats administered urethane 1 h after SE onset as demonstrated by cortical electroencephalography (EEG). By contrast, diazepam interrupted SE but seizures with high power in the 20- to 70-Hz band returned 6-10 h later. Urethane was more effective than diazepam at reducing hippocampal neurodegeneration, brain inflammation, gliosis and weight loss as measured on day 4 after SE. Furthermore, rats administered urethane displayed a 73% reduction in the incidence of spontaneous recurrent seizures after four to eight weeks and a 90% reduction in frequency of seizures in epileptic rats. By contrast, behavioral changes in the light/dark box, open field and a novel object recognition task were not improved by urethane. These findings indicate that in typical rodent SE models, it is the return of SE overnight, and not the initially intense 1-2 h of SE experience, that is largely responsible for neurodegeneration, accompanying inflammation, and the subsequent development of epilepsy.
Keywords: DFP; EEG; diazepam; hippocampus; neurodegeneration; urethane.
Figures






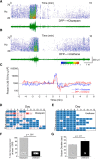
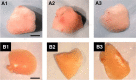
Similar articles
-
Comparison of neuropathology in rats following status epilepticus induced by diisopropylfluorophosphate and soman.Neurotoxicology. 2021 Mar;83:14-27. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2020.12.010. Epub 2020 Dec 19. Neurotoxicology. 2021. PMID: 33352274 Free PMC article.
-
Urethane attenuates early neuropathology of diisopropylfluorophosphate-induced status epilepticus in rats.Neurobiol Dis. 2020 Jul;140:104863. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2020.104863. Epub 2020 Apr 10. Neurobiol Dis. 2020. PMID: 32283202 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of status epilepticus induced by two organophosphates in rats.Epilepsy Res. 2012 Sep;101(3):268-76. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2012.04.014. Epub 2012 May 9. Epilepsy Res. 2012. PMID: 22578704 Free PMC article.
-
Single versus combinatorial therapies in status epilepticus: Novel data from preclinical models.Epilepsy Behav. 2015 Aug;49:20-5. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2015.02.027. Epub 2015 Mar 26. Epilepsy Behav. 2015. PMID: 25819944 Review.
-
Persistent behavior deficits, neuroinflammation, and oxidative stress in a rat model of acute organophosphate intoxication.Neurobiol Dis. 2020 Jan;133:104431. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2019.03.019. Epub 2019 Mar 21. Neurobiol Dis. 2020. PMID: 30905768 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel Second-Generation EP2 Receptor Antagonist Reduces Neuroinflammation and Gliosis After Status Epilepticus in Rats.Neurotherapeutics. 2021 Apr;18(2):1207-1225. doi: 10.1007/s13311-020-00969-5. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Neurotherapeutics. 2021. PMID: 33410110 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of neuropathology in rats following status epilepticus induced by diisopropylfluorophosphate and soman.Neurotoxicology. 2021 Mar;83:14-27. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2020.12.010. Epub 2020 Dec 19. Neurotoxicology. 2021. PMID: 33352274 Free PMC article.
-
Intramuscular atenolol and levetiracetam reduce mortality in a rat model of paraoxon-induced status epilepticus.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2020 Nov;1480(1):219-232. doi: 10.1111/nyas.14500. Epub 2020 Sep 22. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2020. PMID: 32961584 Free PMC article.
-
Gut dysbiosis following organophosphate, diisopropylfluorophosphate (DFP), intoxication and saracatinib oral administration.Front Microbiomes. 2022;1:1006078. doi: 10.3389/frmbi.2022.1006078. Epub 2022 Oct 20. Front Microbiomes. 2022. PMID: 37304619 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroinflammation as a Therapeutic Target for Mitigating the Long-Term Consequences of Acute Organophosphate Intoxication.Front Pharmacol. 2021 May 12;12:674325. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.674325. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34054549 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Borges K, Gearing M, McDermott DL, Smith AB, Almonte AG, Wainer BH, Dingledine R (2003) Neuronal and glial pathological changes during epileptogenesis in the mouse pilocarpine model. Exp Neurol 182:21–34. - PubMed
-
- Brandt C, Töllner K, Klee R, Bröer S, Löscher W (2015) Effective termination of status epilepticus by rational polypharmacy in the lithium-pilocarpine model in rats: window of opportunity to prevent epilepsy and prediction of epilepsy by biomarkers. Neurobiol Dis 75:78–90. 10.1016/j.nbd.2014.12.015 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
