The Effectiveness of Trimetazidine Treatment in Patients with Stable Angina Pectoris of Various Durations: Results from the CHOICE-2 Study
- PMID: 29766461
- PMCID: PMC11343809
- DOI: 10.1007/s12325-018-0674-4
The Effectiveness of Trimetazidine Treatment in Patients with Stable Angina Pectoris of Various Durations: Results from the CHOICE-2 Study
Abstract
Introduction: Trimetazidine (TMZ) has been shown to reduce angina symptoms and to increase exercise capacity in randomized clinical trials, but more extensive data would be useful to assess its effects in real-world clinical practice and in patients with different durations of disease.
Methods: CHOICE-2 was a Russian, multicenter, 6-month, open-label, prospective observational study that assessed the effect of adding TMZ modified release 35 mg bid to antianginal treatment in a real-world setting. The present analysis of CHOICE-2 results explored the effects of adding TMZ to background antianginal therapies with regard to the duration of stable angina.
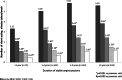
Results: A total of 741 patients with known durations of disease were divided into four groups according to stable angina pectoris (AP) duration, ranging from less than 1 year to more than 9 years. Addition of TMZ led to a significant decrease in the frequency of angina attacks and in the use of short-acting nitrates in all groups. In patients with recently diagnosed angina (AP duration < 1 year), the average number of angina attacks per week decreased significantly from 3.75 ± 4.63 to 0.67 ± 1.51 and in those with advanced disease (AP duration > 9 years) from 5.63 ± 5.24 to 1.32 ± 2.07. Angina-free walking distance also improved significantly. Addition of TMZ also improved patient well-being. Results were achieved rapidly (within 2 weeks), were maintained over 6 months, and were obtained in all patient groups regardless of angina duration.
Conclusion: TMZ added to other antianginal therapies proved to be effective for reducing angina attacks and short-acting nitrate use, increasing angina-free walking distance, and improving patient well-being in a real-life setting, irrespective of angina duration, including patients with recently diagnosed angina. This provides an opportunity for intensification of treatment early on in the disease process, with the aim of decreasing angina burden and improving patient quality of life.
Funding: Servier.
Trial registration: ISRCTN identifier ISRCTN65209863. Plain language summary available for this article.
Keywords: Antianginal combination therapy; Cardiology; Clinical practice; Observational study; Real-world evidence; Stable angina; Trimetazidine.
Conflict of interest statement
Maria Glezer, scientific coordinator of this study, received honoraria for lectures from Servier, Moscow, Russian Federation.
Figures



References
-
- Dargie HJ, Ford I, Fox KM. Total Ischemic Burden European Trial (TIBET). Effects of ischaemia and treatment with atenolol, nifedipine SR and their combination on outcome in patients with chronic stable angina. The TIBET Study Group. Eur Heart J. 1996;17:104–12. 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a014668 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pepine CJ, Handberg EM, Cooper-DeHoff RM, et al. A calcium antagonist vs a non-calcium antagonist hypertension treatment strategy for patients with coronary artery disease. The International Verapamil-Trandolapril Study (INVEST): a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2003;290:2805–16. 10.1001/jama.290.21.2805 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

