Clopidogrel and Aspirin in Acute Ischemic Stroke and High-Risk TIA
- PMID: 29766750
- PMCID: PMC6193486
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1800410
Clopidogrel and Aspirin in Acute Ischemic Stroke and High-Risk TIA
Abstract
Background: Combination antiplatelet therapy with clopidogrel and aspirin may reduce the rate of recurrent stroke during the first 3 months after a minor ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA). A trial of combination antiplatelet therapy in a Chinese population has shown a reduction in the risk of recurrent stroke. We tested this combination in an international population.
Methods: In a randomized trial, we assigned patients with minor ischemic stroke or high-risk TIA to receive either clopidogrel at a loading dose of 600 mg on day 1, followed by 75 mg per day, plus aspirin (at a dose of 50 to 325 mg per day) or the same range of doses of aspirin alone. The dose of aspirin in each group was selected by the site investigator. The primary efficacy outcome in a time-to-event analysis was the risk of a composite of major ischemic events, which was defined as ischemic stroke, myocardial infarction, or death from an ischemic vascular event, at 90 days.
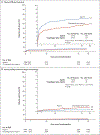
Results: A total of 4881 patients were enrolled at 269 international sites. The trial was halted after 84% of the anticipated number of patients had been enrolled because the data and safety monitoring board had determined that the combination of clopidogrel and aspirin was associated with both a lower risk of major ischemic events and a higher risk of major hemorrhage than aspirin alone at 90 days. Major ischemic events occurred in 121 of 2432 patients (5.0%) receiving clopidogrel plus aspirin and in 160 of 2449 patients (6.5%) receiving aspirin plus placebo (hazard ratio, 0.75; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.59 to 0.95; P=0.02), with most events occurring during the first week after the initial event. Major hemorrhage occurred in 23 patients (0.9%) receiving clopidogrel plus aspirin and in 10 patients (0.4%) receiving aspirin plus placebo (hazard ratio, 2.32; 95% CI, 1.10 to 4.87; P=0.02).
Conclusions: In patients with minor ischemic stroke or high-risk TIA, those who received a combination of clopidogrel and aspirin had a lower risk of major ischemic events but a higher risk of major hemorrhage at 90 days than those who received aspirin alone. (Funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke; POINT ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT00991029 .).
Figures


Comment in
-
Antiplatelet Therapy after Ischemic Stroke or TIA.N Engl J Med. 2018 Jul 19;379(3):291-292. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1806043. Epub 2018 May 16. N Engl J Med. 2018. PMID: 29766754 No abstract available.
-
Positive trials in ischaemic stroke reported at ESOC 2018.Nat Rev Neurol. 2018 Jul;14(7):379. doi: 10.1038/s41582-018-0023-x. Nat Rev Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29858608 No abstract available.
-
Antiplatelet Agents in Acute Stroke and TIA.N Engl J Med. 2018 Oct 25;379(17):e29. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1811048. N Engl J Med. 2018. PMID: 30358973 No abstract available.
-
Antiplatelet Agents in Acute Stroke and TIA.N Engl J Med. 2018 Oct 25;379(17):e29. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1811048. N Engl J Med. 2018. PMID: 30358974 No abstract available.
-
Dual antiplatelet treatment in TIA and high-risk ischemic CVA, a review of the POINT trial.CJEM. 2020 Jan;22(1):29-30. doi: 10.1017/cem.2019.407. CJEM. 2020. PMID: 31566161 No abstract available.
References
-
- Johnston SC, Gress DR, Browner WS, Sidney S. Short-term prognosis after emergency-department diagnosis of transient ischemic attack. JAMA 2000;2 84: 2901–6. - PubMed
-
- Giles MF, Rothwell PM. Risk of stroke early after transient ischaemic attack: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol 2007; 6: 1063–72. - PubMed
-
- Wu CM, McLaughlin K, Lorenzetti DL, Hill MD, Manns BJ, Ghali WA. Early risk of stroke after transient ischemic attack: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Intern Med 2007; 167: 2417–22. - PubMed
-
- Amarenco P, Lavallee PC, Labreuche J, et al. One-year risk of stroke and major cardiovascular events after transient ischemic attack or minor ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 2016; 374: 1533–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
