Tissue Damage Signaling Is a Prerequisite for Protective Neutrophil Recruitment to Microbial Infection in Zebrafish
- PMID: 29768163
- PMCID: PMC6082643
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.04.020
Tissue Damage Signaling Is a Prerequisite for Protective Neutrophil Recruitment to Microbial Infection in Zebrafish
Abstract
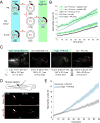
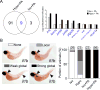
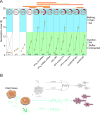
Tissue damage and infection are deemed likewise triggers of innate immune responses. But whereas neutrophil responses to microbes are generally protective, neutrophil recruitment into damaged tissues without infection is deleterious. Why neutrophils respond to tissue damage and not just to microbes is unknown. Is it a flaw of the innate immune system that persists because evolution did not select against it, or does it provide a selective advantage? Here we dissect the contribution of tissue damage signaling to antimicrobial immune responses in a live vertebrate. By intravital imaging of zebrafish larvae, a powerful model for innate immunity, we show that prevention of tissue damage signaling upon microbial ear infection abrogates leukocyte chemotaxis and reduces animal survival, at least in part, through suppression of cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPla2), which integrates tissue damage- and microbe-derived cues. Thus, microbial cues are insufficient, and damage signaling is essential for antimicrobial neutrophil responses in zebrafish.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
Getting DAMP(s) Wets the Whistle for Neutrophil Recruitment.Immunity. 2018 May 15;48(5):846-848. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.04.027. Immunity. 2018. PMID: 29768171
References
-
- Bäckhed F, Ley RE, Sonnenburg JL, Peterson DA, Gordon JI. Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science (80-.) 2005;307:1915–1920. - PubMed
-
- Barton GM, Medzhitov R. Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. Science (80-.) 2003;300:1524–1525. - PubMed
-
- Bloes DA, Kretschmer D, Peschel A. Enemy attraction: bacterial agonists for leukocyte chemotaxis receptors. Nat. Rev. Micro. 2015;13:95–104. - PubMed
-
- Dacheux D, Goure J, Chabert J, Usson Y, Attree I. Pore-forming activity of type III system-secreted proteins leads to oncosis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa-infected macrophages. Mol. Microbiol. 2001;40:76–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

