Clinical efficacy of xenon versus propofol: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 29768360
- PMCID: PMC5976329
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010758
Clinical efficacy of xenon versus propofol: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Interest in the anesthetic use of xenon, a noble gas, has waxed and waned for decades, and the clinical effects of xenon are still debated. We performed a meta-analysis to compare the clinical efficacy of xenon with that of propofol.
Methods: Electronic searches were performed through December 2017 using various databases, including PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library. We identified thirteen trials that included a total of 817 patients.
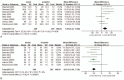
Results: Patients treated with xenon had a lower bispectral index (BIS) (weighted mean difference (WMD): -6.26, 95% confidence interval (CI): -11.33 to -1.18, P = .02), a higher mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) (WMD: 7.00, 95% CI: 2.32-11.68, P = .003) and a lower heart rate (HR) (WMD: -9.45, 95% CI: -12.28 to -6.63, P < 0.00001) than propofol-treated patients. However, there were no significant differences between the 2 treatment groups in the effects of nondepolarizing muscular relaxants, the duration spent in the postanesthesia care unit (PACU) (WMD: -0.94, 95% CI: -8.79-6.91, P = .81), or the incidence of perioperative complications [assessed using the outcomes of postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) (relative risk (RR): 2.01, 95% CI: 0.79-5.11, P = .14), hypotension (RR: 0.62, 95% CI: 0.27 to 1.40, P = .25), hypertension (RR: 1.27, 95% CI: 0.73-2.21, P = .39) and bradycardia (RR: 1.00, 95% CI: 0.36-2.74, P = 1.00)].
Conclusion: In this meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, we found that xenon treatment resulted in a higher MAP, a lower HR, and a smaller BIS index than treatment with propofol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

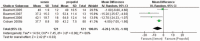


References
-
- Cullen SC, Gross EG. The anesthetic properties of xenon in animals and human beings, with additional observations on krypton. Science 1951;113:580–2. - PubMed
-
- Law LS, LoE A, Gan TJ. Xenon anesthesia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Anesth Analg 2016;122:678–97. - PubMed
-
- Abramo A, Di Salvo C, Baldi G, et al. Xenon anesthesia reduces TNFα and IL10 in bariatric patients. Obes Surg 2012;22:208–12. - PubMed
-
- Baumert JH, Falter F, Eletr D, et al. Xenon anaesthesia may preserve cardiovascular function in patients with heart failure. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 2005;49:743–9. - PubMed
-
- Baumert JH, Hein M, Hecker KE, et al. Xenon or propofol anaesthesia for patients at cardiovascular risk in non-cardiac surgery. Br J Anaesth 2008;100:605–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

