Remote ischemic preconditioning STAT3-dependently ameliorates pulmonary ischemia/reperfusion injury
- PMID: 29768493
- PMCID: PMC5955491
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196186
Remote ischemic preconditioning STAT3-dependently ameliorates pulmonary ischemia/reperfusion injury
Abstract
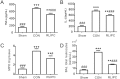
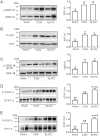
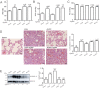
The lungs are highly susceptible to injury, including ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. Pulmonary I/R injury can occur when correcting conditions such as primary pulmonary hypertension, and is also relatively common after lung transplantation or other cardiothoracic surgery. Methods to reduce pulmonary I/R injury are urgently needed to improve outcomes following procedures such as lung transplantation. Remote liver ischemic preconditioning (RLIPC) is an effective cardioprotective measure, reducing damage caused by subsequent cardiac I/R injury, but little is known about its potential role in pulmonary protection. Here, we analyzed the efficacy and mechanistic basis of RLIPC in a rat model of pulmonary I/R injury. RLIPC reduced lung I/R injury, lessening structural damage, inflammatory cytokine production and apoptosis. In addition, RLIPC preserved pulmonary function compared to controls following lung I/R injury. RLIPC stimulated phosphorylation of pulmonary STAT3, a component of the SAFE signaling pathway, but not phosphorylation of RISK pathway signaling proteins. Accordingly, STAT3 inhibition using AG490 eliminated the pulmonary protection afforded by RLIPC. Our data demonstrate for the first time that RLIPC protects against pulmonary I/R injury, via a signaling pathway requiring STAT3 phosphorylation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Braunwald E, Kloner RA. Myocardial reperfusion: a double-edged sword? The Journal of clinical investigation. 1985;76(5):1713–9. doi: 10.1172/JCI112160 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Templeton AW, Garrotto LJ. Acquired extracardiac causes of pulmonary ischemia. Dis Chest. 1967;51(2):166–71. . - PubMed
-
- den Hengst WA, Gielis JF, Lin JY, Van Schil PE, De Windt LJ, Moens AL. Lung ischemia-reperfusion injury: a molecular and clinical view on a complex pathophysiological process. American journal of physiology Heart and circulatory physiology. 2010;299(5):H1283–99. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00251.2010 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Weyker PD, Webb CA, Kiamanesh D, Flynn BC. Lung ischemia reperfusion injury: a bench-to-bedside review. Semin Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2013;17(1):28–43. doi: 10.1177/1089253212458329 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Garcia-de-la-Asuncion J, Garcia-del-Olmo E, Perez-Griera J, Marti F, Galan G, Morcillo A, et al. Oxidative lung injury correlates with one-lung ventilation time during pulmonary lobectomy: a study of exhaled breath condensate and blood. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2015;48(3):e37–44. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezv207 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

