Infectious syphilis in Canada: 2003-2012
- PMID: 29769929
- PMCID: PMC5864306
- DOI: 10.14745/ccdr.v41i02a03
Infectious syphilis in Canada: 2003-2012
Abstract
Background: In the 1990s, rates of reported cases of infectious syphilis were relatively low and were similar among males and females. In 2001, rates began to increase, particularly among males.
Objective: To identify trends in reported cases of infectious syphilis in Canada from January 1, 2003 to December 31, 2012.
Methods: Notifiable disease reports were submitted to the Public Health Agency of Canada by provincial and territorial epidemiological units and data were summarized by age and sex.
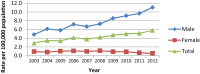
Results: Rates of reported cases of infectious syphilis increased by 101.0% between 2003 and 2012, from 2.9 to 5.8 per 100,000. Over this time frame, rates increased among males by 128.3% and decreased among females by 40.9%. In males, rates of infectious syphilis were highest among those aged 25 to 29; in females, rates were highest among those aged 20 to 24.
Conclusion: In Canada, as in many countries, rates of reported infectious syphilis cases in males have markedly increased over the last 10 years.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None
Figures
References
-
- Expert Working Group for the Canadian Guidelines on Sexually Transmitted Infections. Syphilis. In: Wong T, Latham-Carmanico C, editors. Canadian guidelines on sexually transmitted infections. 2010 ed. Ottawa: Public Health Agency of Canada; 2010.
-
- Pialoux G, Vimont S, Moulignier A, Buteux M, Abraham B, Bonnard P. Effect of HIV infection on the course of syphilis. AIDS Rev 2008. Apr-Jun;10(2):85–92. - PubMed
-
- Narula T, Kamboj S, Martinez J, Engel LS. Co-infection: HIV and the great mimic syphilis. HIV Clin 2010;22(2):7–10. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources