Crosstalk Between the Unfolded Protein Response, MicroRNAs, and Insulin Signaling Pathways: In Search of Biomarkers for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 29770126
- PMCID: PMC5940743
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00210
Crosstalk Between the Unfolded Protein Response, MicroRNAs, and Insulin Signaling Pathways: In Search of Biomarkers for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
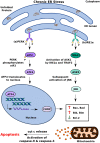
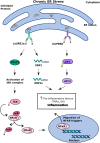
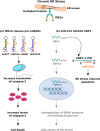
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a metabolic disorder that is characterized by functional defects in glucose metabolism and insulin secretion. Its complex etiology and multifaceted nature have made it difficult to design effective therapies for early diagnosis and treatment. Several lines of evidence indicate that aberrant activation of the unfolded protein response (UPR) in response to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress impairs the β cell's ability to respond to glucose and promotes apoptosis. Elucidating the molecular mechanisms that govern β cell dysfunction and cell death can help investigators design therapies to halt or prevent the development of T2DM. Early diagnosis of T2DM, however, warrants additionally the identification of potential biomarkers. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are key regulators of transcriptional processes that modulate various features of insulin signaling, such as insulin sensitivity, glucose tolerance, and insulin secretion. A deeper understanding of how changes in patterns of expression of miRNAs correlate with altered glucose metabolism can enable investigators to develop methods for the early diagnosis and treatment of T2DM. The first part of this review examines how altered expression of specific UPR pathway proteins disrupts ER function and causes β cell dysfunction, while the second part discusses the potential role of miRNAs in the diagnostic and treatment of T2DM.
Keywords: biomarkers; endoplasmic reticulum stress; microRNAs; type 2 diabetes; unfolded protein response.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. World Health Day 2016: Diabetes. New Delhi: SEARO. World Health Organization, South-East Asia Regional Office; (2016). Available from: http://www.searo.who.int/india/mediacentre/events/2016/en/
-
- World Health Organization. WHO | Diabetes. WHO; (2016). Available from: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs312/en/ (Accessed: November 2017).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

