Genetic Biomarkers Of Sensitivity and Resistance to Venetoclax Monotherapy in Patients With Relapsed Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- PMID: 29770480
- PMCID: PMC6120451
- DOI: 10.1002/ajh.25146
Genetic Biomarkers Of Sensitivity and Resistance to Venetoclax Monotherapy in Patients With Relapsed Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Keywords: AML; BLC-2; Venetoclax.
Figures
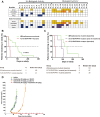
References
-
- Mali RS, Laseter EA, Doyle K, et al. FLT3‐ITD activation mediates resistance to the BCL‐2 selective antagonist, venetoclax, in FLT3‐ITD mutant AML models. Blood. 2017;130:1348.
-
- Yoshimi A, Lin KT, Wiseman D, et al. Spliceosomal dysfunction is a critical mediator of IDH2 mutant leukemogenesis. Blood. 2017;130:473.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
