Plasmodial Kinase Inhibitors: License to Cure?
- PMID: 29771541
- PMCID: PMC6166223
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b00329
Plasmodial Kinase Inhibitors: License to Cure?
Abstract
Advances in the genetics, function, and stage-specificity of Plasmodium kinases has driven robust efforts to identify targets for the design of antimalarial therapies. Reverse genomics following phenotypic screening against Plasmodia or related parasites has uncovered vulnerable kinase targets including PI4K, PKG, and GSK-3, an approach bolstered by access to human disease-directed kinase libraries. Alternatively, screening compound libraries against Plasmodium kinases has successfully led to inhibitors with antiplasmodial activity. As with other therapeutic areas, optimizing compound ADMET and PK properties in parallel with target inhibitory potency and whole cell activity becomes paramount toward advancing compounds as clinical candidates. These and other considerations will be discussed in the context of progress achieved toward deriving important, novel mode-of-action kinase-inhibiting antimalarial medicines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures






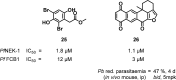
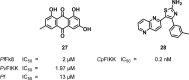
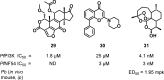
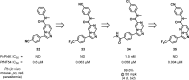

References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) . World Malaria Report. http://www.who.int/malaria/publications/world-malaria-report-2017/report... (accessed Feb 19, 2018).
-
- Dondorp A. M.; Nosten F.; Yi P.; Das D.; Phyo A. P.; Tarning J.; Lwin K. M.; Ariey F.; Hanpithakpong W.; Lee S. J.; Ringwald P.; Silamut K.; Imwong M.; Chotivanich K.; Lim P.; Herdman T.; An S. S.; Yeung S.; Singhasivanon P.; Day N. P. J.; Lindegardh N.; Socheat D.; White N. J. Artemisinin Resistance in Plasmodium Falciparum Malaria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361 (5), 455–467. 10.1056/NEJMoa0808859. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

